Uveitis
Iritis; Pars planitis; Choroiditis; Chorioretinitis; Anterior uveitis; Posterior uveitis; Iridocyclitis
Uveitis is swelling and inflammation of the uvea. The uvea is the middle layer of the wall of the eye. The uvea supplies blood for the iris at the front of the eye and the retina in the back of the eye.
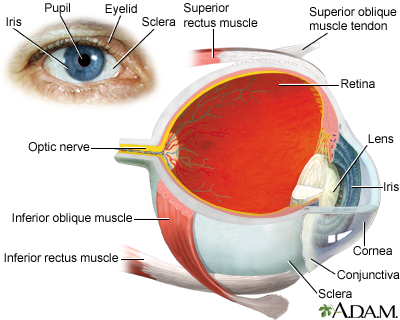
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
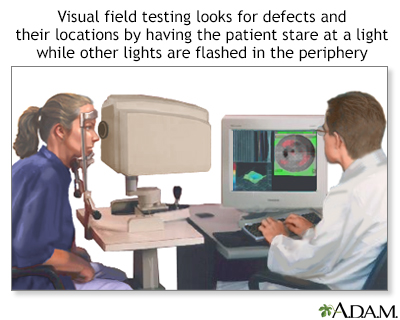
Central and peripheral vision is tested by using visual field tests. Changes may indicate eye diseases, such as glaucoma or retinitis.
Causes
Uveitis can be caused by autoimmune disorders. These diseases occur when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. Examples are:
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Behcet disease
- Psoriasis
- Reactive arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Ulcerative colitis
Uveitis can also be caused by infections such as:
- AIDS
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis
- Herpes zoster infection
- Histoplasmosis
- Kawasaki disease
- Syphilis
- Toxoplasmosis
Exposure to toxins or injury can also cause uveitis. In many cases, the cause is unknown.
Often the inflammation is limited to only part of the uvea. The most common form of uveitis involves inflammation of the iris, in the front part of the eye. In this case, the condition is called iritis. In most cases, it occurs in healthy people. The disorder may affect only one eye. It is most common in young and middle-aged people.
Posterior uveitis affects the back part of the eye. It involves primarily the choroid. This is the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue in the middle layer of the eye. This type of uveitis is called choroiditis. If the retina is also involved, it is called chorioretinitis.
Another form of uveitis is pars planitis. Inflammation occurs in the area called the pars plana, which is located between the iris and the choroid. Pars planitis most often occurs in young men. It is generally not associated with any other disease. However, it may be linked to Crohn disease and possibly multiple sclerosis.
Symptoms
Uveitis can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms depend on which part of the uvea is inflamed. Symptoms may develop rapidly and can include:
- Blurred vision
- Dark, floating spots in the vision
- Eye pain
- Redness of the eye
- Sensitivity to light
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will take a complete medical history and do an eye exam. Lab tests may be done to rule out infection or a weak immune system.
If you are over age 25 and have pars planitis, your provider will suggest a brain and spine MRI. This will rule out multiple sclerosis.
Treatment
Iritis and irido-cyclitis (anterior uveitis) are most often mild. Treatment may involve:
- Dark glasses
- Eye drops that dilate the pupil to relieve pain
- Steroid eye drops
Pars planitis is often treated with steroid eye drops. Other medicines, including steroids taken by mouth, may be used to help suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Posterior uveitis treatment depends on the underlying cause. It almost always includes steroids taken by mouth.
If the uveitis is caused by a body-wide (systemic) infection, you may be given antibiotics. You may also be given powerful anti-inflammatory medicines called corticosteroids. Sometimes certain types of immune-suppressant drugs are used to treat severe uveitis.
Outlook (Prognosis)
With proper treatment, most attacks of anterior uveitis go away in a few days to weeks. However, the problem often returns.
Posterior uveitis may last from months to years. It may cause permanent vision damage, even with treatment.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Cataracts
- Fluid within the retina
- Glaucoma
- Irregular pupil
- Retinal detachment
- Vision loss
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Symptoms that need urgent medical care are:
- Eye pain
- Reduced vision
Prevention
If you have a body-wide (systemic) infection or disease, treating the condition may prevent uveitis.
References
American Academy of Ophthalmology. Treatment of uveitis.
Cioffi GA, Liebmann JM. Diseases of the visual system. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 395.
Durand ML. Infectious causes of uveitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 115.
Gery I, Chan C-C. Mechanisms of uveitis. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 7.2.
Read RW. General approach to the uveitis patient and treatment strategies. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 7.3.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 8/22/2022
Reviewed by: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
