Disseminated tuberculosis
Miliary tuberculosis; Tuberculosis - disseminated; Extrapulmonary tuberculosis
Disseminated tuberculosis is a mycobacterial infection in which mycobacteria have spread from the lungs to other parts of the body through the blood or lymph system.
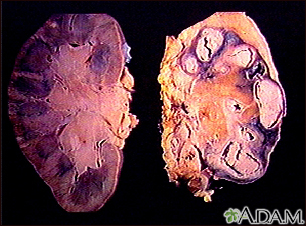
Kidneys can be damaged by tuberculosis. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but may cause infection in many other organs in the body. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
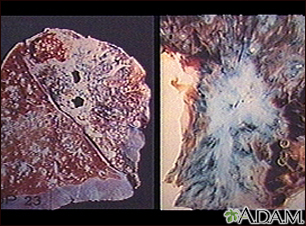
Tuberculosis is caused by a group of organisms, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M bovis, M africanum and a few other rarer subtypes. Tuberculosis usually appears as a lung (pulmonary) infection. However, it may infect other organs in the body. Recently, antibiotic-resistant strains of tuberculosis have appeared. With increasing numbers of immunocompromised individuals with AIDS, and homeless people without medical care, tuberculosis is seen more frequently today. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
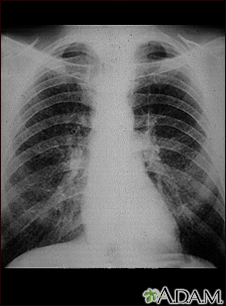
This chest x-ray shows coal worker's lungs. There are diffuse, small, light areas on both sides (1 to 3 mm) in all parts of the lungs. Diseases that may result in an x-ray like this include simple coal workers pneumoconiosis (CWP) - stage I, simple silicosis, miliary tuberculosis, histiocytosis X (eosinophilic granuloma), and other diffuse infiltrate pulmonary diseases.
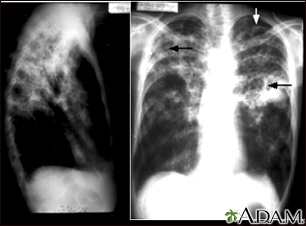
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that causes inflammation, the formation of tubercles and other growths within tissue, and can cause tissue death. These chest X-rays show advanced pulmonary tuberculosis. There are multiple light areas (opacities) of varying size that run together (coalesce). Arrows indicate the location of cavities within these light areas. The X-ray on the left clearly shows that the opacities are located in the upper area of the lungs toward the back. The appearance is typical for chronic pulmonary tuberculosis but may also occur with chronic pulmonary histiocytosis and chronic pulmonary coccidioidomycosis. Pulmonary tuberculosis is making a comeback with new resistant strains that are difficult to treat. Pulmonary tuberculosis is the most common form of the disease, but other organs can be infected.
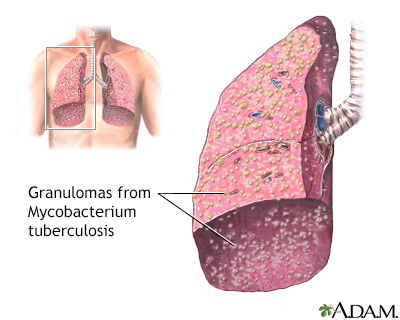
Miliary tuberculosis is characterized by a chronic, contagious bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis that has spread to other organs of the body by the blood or lymph system.
Causes
Tuberculosis (TB) infection can develop after breathing in droplets sprayed into the air from a cough or sneeze by someone infected with the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium. The resulting lung infection is called primary TB.
The usual site of TB is the lungs (pulmonary TB), but other organs can be involved. In the United States, most people with primary tuberculosis get better and have no further evidence of disease. Disseminated TB develops in the small number of infected people whose immune systems do not successfully contain the primary infection.
Disseminated disease can occur within weeks of the primary infection. Sometimes, it occurs years after you become infected. You are more likely to get this type of TB if you have a weakened immune system due to disease (such as AIDS) or certain medicines. Infants and older adults are also at higher risk.
Your risk of catching TB increases if you:
- Are around people who have the disease (such as during overseas travel)
- Live in crowded or unclean conditions
- Have poor nutrition
The following factors can increase the rate of TB infection in a population:
- Increase in HIV infections
- Increase in number of homeless people with unstable housing (poor environment and nutrition)
- The appearance of drug-resistant strains of TB
Symptoms
Disseminated tuberculosis can affect many different body areas. Symptoms depend on the affected areas of the body and can include:
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Chills
- Cough and shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Fever
- General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling (malaise)
- Joint pain
- Pale skin due to anemia (pallor)
- Sweating
- Swollen glands
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may show:
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Biopsies and cultures of affected organs or tissues
- Bronchoscopy for biopsy or culture
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the affected area
- Fundoscopy may reveal retinal lesions
- Interferon-gamma release blood test, such as the QFT-Gold test to test for prior exposure to TB
- Lung biopsy
- Mycobacterial culture of bone marrow or blood
- Pleural biopsy
- Tuberculin skin test (PPD test)
- Sputum examination and cultures
- Thoracentesis
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to cure the infection with medicines that fight the TB bacteria. Treatment of disseminated TB involves a combination of several medicines (usually 4). All medicines are continued until lab tests show which work best.
You may need to take many different pills for 6 months or longer. It is very important that you take the pills the way your provider instructed.
When people do not take their TB medicines as instructed, the infection can become much more difficult to treat. The TB bacteria can become resistant to treatment. This means the medicines no longer work.
When there is concern that a person may not take all the medicines as directed, a provider may need to watch the person take the prescribed medicines. This approach is called directly observed therapy. In this case, medicines may be given 2 or 3 times a week, as prescribed by a provider.
You may need to stay at home or be admitted to a hospital for 2 to 4 weeks to avoid spreading the disease to others until you are no longer contagious.
Your provider may be required by law to report your TB illness to the local health department. Your health care team will ensure that you receive the best care.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most forms of disseminated TB respond well to treatment. The tissue that is affected, such as the bones or joints, may have permanent damage due to the infection.
Possible Complications
Complications of disseminated TB can include:
- Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Liver inflammation
- Lung failure
- Return of the disease
Medicines used to treat TB can cause side effects, including:
- Changes in vision
- Orange- or brown-colored tears and urine
- Rash
- Liver inflammation
A vision test may be done before treatment so your doctor can monitor any changes in the health of your eyes.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you know or suspect that you have been exposed to TB. All forms of TB and exposure need prompt evaluation and treatment.
Prevention
TB is a preventable disease, even in those who have been exposed to an infected person. Skin testing for TB is used in high-risk populations or in people who may have been exposed to TB, such as health care workers.
People who have been exposed to TB should be skin tested immediately and have a follow-up test at a later date, if the first test is negative.
A positive skin test means you have come into contact with the TB bacteria. It does not mean that you have active disease or are contagious. Talk to your doctor about how to prevent getting tuberculosis.
Prompt treatment is extremely important in controlling the spread of TB from those who have active TB disease to those who have never been infected with TB.
Some countries with a high incidence of TB give people a vaccination (called BCG) to prevent TB. The effectiveness of this vaccine is limited and it is not routinely used in the United States.
People who have had BCG may still be skin tested for TB. Discuss the test results (if positive) with your provider.
References
Ellner JJ, Jacobson KR. Tuberculosis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 308.
Fitzgerald DW, Sterling TR, Haas DW. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 249.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 11/23/2021
Reviewed by: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
