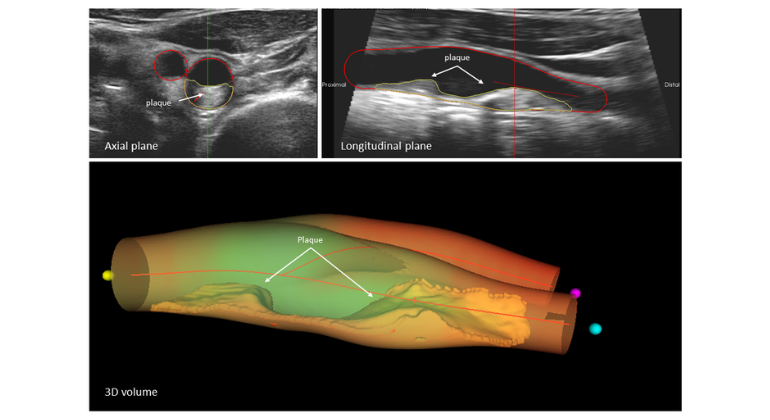
Inexpensive Drug Costing Less Than Three Dollars May Minimize Damage from Heart Attack
Collaborative study by Spain and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai shows potential benefits of administering beta-blocker medication to heart attack patients in ambulance.
Early treatment of heart attack patients with an inexpensive beta-blocker drug called metoprolol, while in transit to the hospital, can significantly reduce damage to the heart during a myocardial infarction, according to clinical trial study results published Oct. 1 in the journal Circulation. The study was a collaboration between Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (CNIC) in Spain and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York.
The study, involving emergency ambulances and seven hospitals across Spain, shows this simple, low-cost intervention strategy with metoprolol could be easily extended throughout the world, to provide significant clinical benefit and could change current treatment practice for heart attack patients. Currently, patients receive no medication before undergoing routine angioplasty, the standard treatment for removing a heart blockage that causes a heart attack and damages heart tissue.
Borja Ibáñez, MD, PhD, head of the Experimental Cardiology Group at CNIC and clinical cardiologist at the Hospital Clínico San Carlos in Spain, is the joint lead investigator of this novel study with Valentín Fuster, MD, PhD, General Director of CNIC, who also serves as Director of Mount Sinai Heart and Physician-in-Chief at The Mount Sinai Medical Center. Also, Dr. Fuster will begin his term in 2014 as the next Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
Metoprolol, a drug of the beta-blocker family, has been available for more than 30 years to treat arterial hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions. In this new study, the team of researchers were able to examine the potential usefulness of metoprolol after a heart attack. The clinical trial named METOCARD-CNIC is the first to test metoprolol therapy, at a cost less than three dollars (or less than two euros), in heart attack patients undergoing standard angioplasty treatment procedures.
According to researchers, the potential savings from this medical therapy intervention may go far beyond the low cost of metoprolol itself, since patients experiencing less-extensively damaged heart muscle are less likely to need more costly treatments such as an implantable defibrillator or to require costly hospitalization for treatment of heart failure. Dr. Ibáñez explains, "the savings in healthcare costs will run into millions; a per-patient outlay of less than two euros (or less than three dollars) will over the years save thousands." Currently, researchers are now carrying out a cost-effectiveness analysis to give a firm estimate of the expected savings.
An acute myocardial infarction, or heart attack, is caused by a sudden obstruction of one of the coronary arteries. A blockage requires immediate medical attention and the response time is critical. With every minute that the artery is blocked, the cells of the heart die becoming necrotic, in exponentially growing numbers. According to researchers, the best strategy for limiting the size of an infarct is to carry out the angioplasty procedure as soon as possible. A delay in reopening the coronary artery could mean a larger region of damaged or necrotic tissue. When necrosis is extensive, the heart loses a large part of its pumping strength, which does not recover.
In addition to the high risk of death during the infarction, survivors are likely to suffer from heart failure and severe arrhythmias, and often may die in the months or years following the attack. "The larger the infarct (death of cardiac muscle), the greater the probability that survivors will suffer these complications in the future," says co-lead investigator Dr. Fuster, who also serves as Director of the Zena and Michael A. Wiener Cardiovascular Institute and the Marie-Josée and Henry R. Kravis Center for Cardiovascular Health at The Mount Sinai Medical Center.
Therefore, Dr. Fuster stresses reducing the amount of tissue that is damaged or dies during an infarction is of the utmost importance. Over the last several decades investigators have searched unsuccessfully for a complementary therapy that would further reduce the extent of heart damage.
A total of 270 patients with infarction were recruited since 2010 in four of Spain's regions including: Madrid, Galicia, León, and Cantabria. In the randomized study, patients were assigned to receive either intravenous metoprolol or a placebo treatment at the moment of diagnosis of a myocardial infarction during ambulance transit to the catheterization laboratory. Hospitals in Spain participating in the METOCARD-CNIC trial included: Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Hospital de La Princesa, Hospital 12 de Octubre, Hospital Puerta de Hierro, and Hospital Quirón (Madrid), Hospital Meixoeiro (Galicia), Hospital de León (León), and Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla (Cantabria).
The efficacy of the medical intervention was evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) a week after the infarction. MRI measured the mass of damaged heart tissue in all patients. The results showed patients who received metoprolol had much smaller infarcts than those who received the control treatment, and that this smaller infarct size was linked to greater heart contractility.
"MRI is a unique tool for studying heart tissue that enables us to explore in exquisite detail heart function, necrosis, the state of the microcirculation, and many other parameters that are critical in determining the post-infarction status of the myocardium," says Dr. Fuster.
The MRI scans were analyzed at the central CNIC laboratory by cardiologists blinded to the treatment. The CNIC team of cardiologists are experts in this analysis, and most of them received their training from Dr. Fuster at The Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York through a bilateral training agreement with the CNIC.
Initial research investigations about the potential benefits of metoprolol were first launched at The Mount Sinai Medical Center in 2006 while Dr. Ibáñez was working there with Dr. Fuster and Mount Sinai's Juan Badimon, PhD, Director of the Atherothrombosis Research Unit at its Cardiovascular Institute. Their preclinical research findings about metoprolol in animal models, analyzed using MRI and published in the journal Circulation in 2007, showed early administration of metoprolol during heart attack increased myocardial salvage and led to the translational medicine potential for human clinical trial.
The research team is currently investigating the molecular mechanism underlying the therapeutic action of metoprolol. Antonio Fernández-Ortiz, MD, PhD, co-investigator on the METOCARD-CNIC study and leader of this sub-study, explains that "this project analyzes the effect of metoprolol on the interaction of blood platelets with inflammatory cells, which might explain the benefit of early treatment with this drug as soon as possible after diagnosis of a heart attack."
Researchers are planning to extend the clinical trial to a much larger number of patients in a multinational study, to demonstrate not only a reduced infarct size, but also a reduced mortality in patients who receive early metoprolol during transit to hospital. The CNIC research team, colleagues in the emergency services, and hospitals are already working on the logistics of a new international clinical trial.
In an editorial accompanying the published article in Circulation, experts from the Technische Universität and the Munich Heart Alliance, Gjin Ndrepepa and Adnan Kastrati, affirmed that, if confirmed by a subsequent analysis of large numbers of patients, the results of METOCARD-CNIC trial are likely to lead to a change in clinical practice: "In this regard, a pharmaco-protective strategy able to reduce infarct size by 20 percent when used in conjunction with primary PCI nurtures great hope in clinical benefit."
In addition, Dr. Ibáñez adds: "the professionals of the emergency ambulance services were the driving force of this study. Their hard work is a professional and human example to us all; we are deeply humbled by the readiness of so many professionals to commit themselves 24 hours a day, 365 days a year to an altruistic project."
Funding for this METOCARD-CNIC clinical trial study was received from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, a competitive research grant from the CNIC, and the assignation of CNIC as a Severo Ochoa center in 2011. Additionally, support was received from the Spanish Ministry of Health, Social Services and Equality, Philips, the Fundación Mutua Madrileña, and from members of the Pro-CNIC Foundation, which manages private contributions to the CNIC.
About The Mount Sinai Medical Center
The Mount Sinai Medical Center encompasses both The Mount Sinai Hospital and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Established in 1968, the Icahn School of Medicine is one of the leading medical schools in the United States, with more than 3,400 faculty in 32 departments and 14 research institutes. It ranks among the top 20 medical schools both in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and by U.S. News & World Report. The Mount Sinai Hospital, founded in 1852, is a 1,171-bed tertiary- and quaternary-care teaching facility and one of the nation's oldest, largest and most-respected voluntary hospitals. The Mount Sinai Hospital is nationally ranked by U.S. News & World Report as one of the top 25 hospitals in 7 specialties based on reputation, safety, and other patient-care factors.
For more information, visit http://www.mountsinai.org/.
Find Mount Sinai on:
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/mountsinainyc
Twitter @mountsinainyc
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with 48,000 employees working across eight hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2024-2025.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
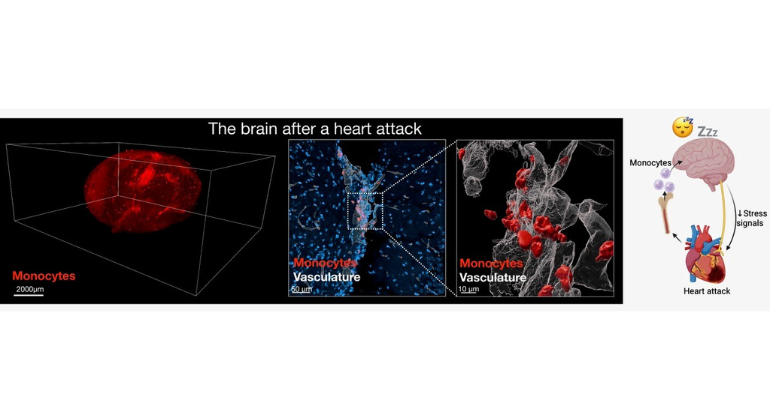
After a Heart Attack, the Heart Signals to the Brain to Increase Sleep to Promote Healing
Oct 30, 2024 View All Press Releases