Mount Sinai Scientists Find Unprecedented Microbial Diversity in Isolated Amazonian Tribe
Scientists from the Icahn School of Medicine have discovered the most diverse collection of bacteria yet in humans among an isolated tribe of Yanomami Amerindians in the remote Amazonian jungles of Venezuela.
Scientists from the Icahn School of Medicine, collaborating with a multicenter team of U.S. and Venezuelan researchers, have discovered the most diverse collection of bacteria yet in humans among an isolated tribe of Yanomami Amerindians in the remote Amazonian jungles of Venezuela. Bacterial diversity in the Yanomami, previously unexposed to antibiotics or industrialized diets, was found to be nearly double that of people living in industrialized countries, and was also significantly higher than in other remote populations moderately exposed to modern practices. The team published its findings today in the journal Science Advances.
The results suggest that antibiotic usage or western diet are linked to the reduced bacterial diversity observed in modern societies, and that this loss of diversity happens quickly upon initial exposure to those practices. “There is a gradient of bacterial diversity that appears to be inversely correlated with exposure to modern practices, such as antibiotics, C-section, or processed foods,” said Jose C. Clemente, PhD, Assistant Professor of Genetics and Genomics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and first author of the study. “Even minimal exposure to these practices greatly decreases diversity and removes potentially beneficial bacteria from our microbiome.”
To date, the vast majority of studies on the human microbiome—the trillions of bacteria harbored in the body that are essential to our well-being—have focused on Western populations. “Characterizing the bacterial communities of non-Western, unexposed populations is essential to understand how the microbiome changes and adapts to westernization,” said Dr. Clemente, “and how those changes might be driving the increased incidence of diseases linked to imbalances in the microbiome.”
The Yanomami villagers of this study, who have subsisted as hunters-and-gatherers for hundreds of generations, are believed to have lived in total seclusion from Western civilization until 2009 when they were first contacted by a medical expedition. Among a rare population of people unexposed to modern antibiotics, the villagers offer a unique window onto the human microbiome.
“We have found unprecedented diversity in fecal, skin, and oral samples collected from the Yanomami villagers,” said Maria Dominguez-Bello, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine at NYU Langone Medical Center and the senior author of the study. “Our results bolster a growing body of data suggesting a link between, on the one hand, decreased bacterial diversity, industrialized diets, and modern antibiotics, and on the other, immunological and metabolic diseases—such as obesity, asthma, allergies, and diabetes, which have dramatically increased since the 1970s,” said Dr. Dominguez-Bello.
The analysis of gut and oral bacteria also revealed that the Yanomami villagers had bacteria encoding antibiotic resistance genes, despite their lack of previous exposure to antibiotics. Surprisingly, the bacterial genes conferred resistance not only to natural antibiotics, such as those produced by soil microbes, but also to synthetic antibiotics.
“During the 1940s and 1950s, in the heyday of pharmaceutical antibiotic development, most antibiotics were derived from naturally occurring bacteria in the soil,” said co-author Gautam Dantas, PhD, Associate Professor of Pathology, Immunology, and Biomedical Engineering at Washington University School of Medicine. “So, we would expect that natural resistance to antibiotics would emerge over millions of years of evolution,” he said. “We didn’t expect to find resistance to modern synthetic antibiotics.” The presence of resistance genes in microbiota unexposed to antibiotics may help explain the rapid rate at which bacteria develop resistance to new classes of antibiotics, noted Dr. Dantas.
“The results from this study have given us a much better understanding of our microbial past,” said Dr. Clemente. “Characterizing now the functions encoded in those bacteria that we are missing will provide further insights into the mechanisms behind these immune and metabolic conditions, and potentially guide us in the development of new therapeutics.”
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with 48,000 employees working across eight hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2024-2025.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.

Mount Sinai Researchers Uncover Why Some Leukemia Cells May Resist Treatment
Oct 30, 2024 View All Press Releases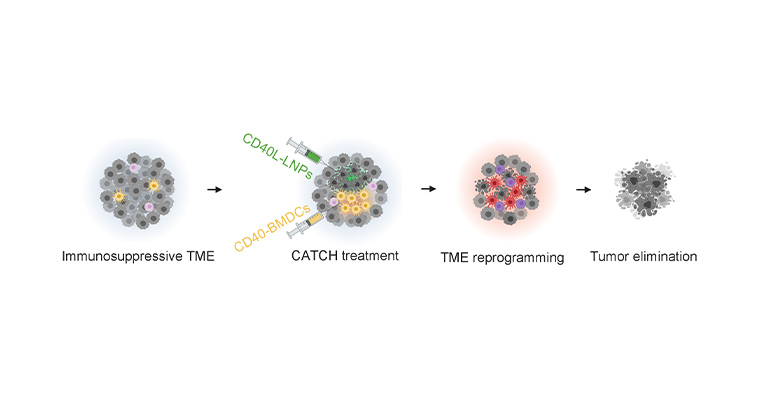
New RNA-based Therapy Combats Melanoma in Mouse Models
Jul 27, 2023 View All Press Releases
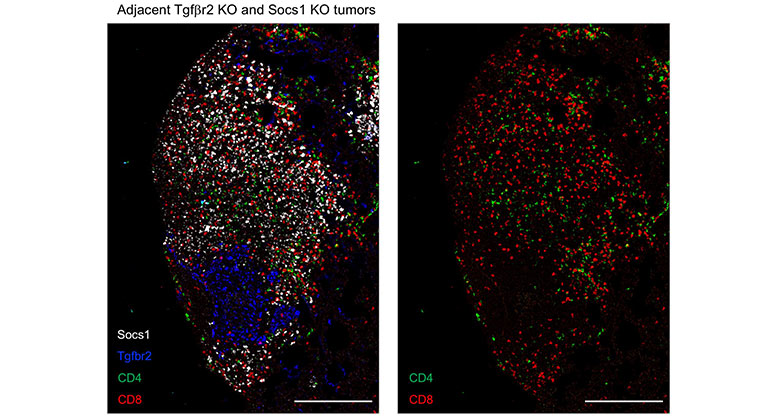
Targeting One Type of Immune Cell With Another Slows Cancer Growth in Preclinical Studies
Oct 25, 2022 View All Press Releases
Novel CRISPR Imaging Technology Reveals Genes Controlling Tumor Immunity
Mar 15, 2022 View All Press ReleasesMount Sinai Researchers: Why COVID-19 May Be Less Common in Children Than Adults
May 22, 2020 View All Press Releases