Spinal stenosis
Pseudo-claudication; Central spinal stenosis; Foraminal spinal stenosis; Degenerative spine disease; Back pain - spinal stenosis; Low back pain - stenosis; LBP - stenosis
Spinal stenosis is narrowing of the spinal column that causes pressure on the spinal cord, or narrowing of the openings (called neural foramina) where spinal nerves leave the spinal column.
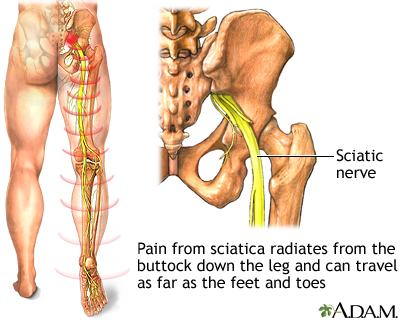
The main nerve traveling down the leg is the sciatic nerve. Pain associated with the sciatic nerve usually originates higher along the spinal cord when nerve roots become compressed or damaged from narrowing of the vertebral column or from a slipped disk. Symptoms can include tingling, numbness, or pain, which radiates to the buttocks legs and feet.
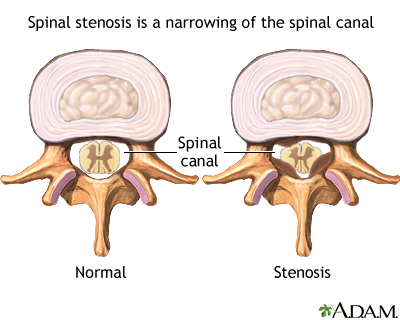
Spinal stenosis is narrowing of the spinal canal. This can develop as you age from drying out and shrinking of the disk spaces. (The disks are 80% water.) If this happens, even a minor injury can cause inflammation of the disk and put pressure on the nerve. You can feel pain anywhere along your back or leg(s) that this nerve supplies.
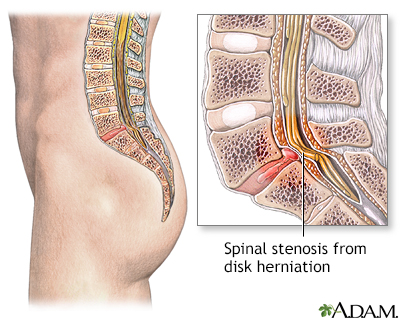
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the lumbar or cervical spinal canal. The narrowing can cause compression on nerve roots resulting in pain or weakness of the legs. Medications or steroid injections are often administered to reduce inflammation. If the pain is persistent and does not respond to these conservative measures, surgery is considered to relieve the pressure on the nerves.
Causes
Spinal stenosis usually occurs as a person ages, however, some people are born with less space for their spinal cord.
- The spinal disks become drier and start to bulge and can rupture.
- The bones and ligaments of the spine thicken or grow larger. This is caused by arthritis or long-term swelling.
Spinal stenosis may also be caused by:
- Arthritis of the spine, usually in middle-aged or older people
- Bone diseases, such as Paget disease
- Defect or growth in the spine that was present from birth
- Narrow spinal canal that the person was born with
- Herniated or slipped disk, which often may have happened in the past
- Injury that causes pressure on the nerve roots or the spinal cord
- Tumors in the spine
- Fracture or injury of a spinal bone
Symptoms
Symptoms often get worse slowly over time. Most often, symptoms will be on one side of the body, but may involve both legs.
Symptoms include:
- Numbness, cramping, or pain in the back, buttocks, thighs, or calves, or in the neck, shoulders, or arms
- Weakness of part of a leg or arm
Symptoms are more likely to be present or get worse when you stand or walk. They often lessen or disappear when you sit down or lean forward. Most people with spinal stenosis cannot walk for a long period without having significant pain.
More serious symptoms include:
- Difficulty or poor balance when walking
- Problems controlling urine or bowel movements
Exams and Tests
During a physical exam, your health care provider will try to find the location of the pain and learn how it affects your movement. You will be asked to:
- Sit, stand, and walk. While you walk, your provider may ask you to try walking on your toes and then your heels.
- Bend forward, backward, and sideways. Your pain may worsen with these movements.
- Lift your legs straight up while lying down. If the pain is worse when you do this, you may have sciatica, especially if you also feel numbness or tingling in one of your legs.
Your provider will also move your legs in different positions, including bending and straightening your knees. This is to check your strength and ability to move.
To test nerve function, your provider will use a rubber hammer to check your reflexes. To test how well your nerves sense feeling, your provider will touch your legs in many places with a pin, cotton swab, or feather. To check your balance, your provider will ask you to close your eyes while standing and keeping your feet together.
A brain and nervous system (neurologic) exam helps confirm leg weakness and loss of sensation in the legs. You may have the following tests:
Treatment
Your provider and other health professionals will help you manage your pain and keep you as active as possible.
- Your provider may refer you for physical therapy. The physical therapist will teach you stretches and exercises that make your back muscles stronger.
- You may also see a chiropractor, a massage therapist, and someone who performs acupuncture. Sometimes, a few visits will help your back or neck pain.
- Cold packs and heat therapy may help your pain during flare-ups.
Treatments for back pain caused by spinal stenosis include:
- Medicines to help relieve back pain.
- A type of talk therapy called cognitive behavioral therapy to help you better understand your pain and teach you how to manage back pain.
- An epidural spinal injection which involves injecting medicine directly into the space around your spinal nerves or spinal cord.
Spinal stenosis symptoms often become worse over time, but this may happen slowly. If the pain does not respond to these treatments, or you lose movement or feeling, you may need surgery.
- Surgery is done to relieve pressure on the nerves or spinal cord.
- You and your provider can decide when you need to have surgery for these symptoms.
Surgery may include removing a bulging disk, removing part of the vertebra bone, or widening the canal and openings where your spinal nerves are located.
During some spinal surgeries, the surgeon will remove some bone to create more room for your spinal nerves or spinal column. The surgeon will then fuse some of the spine bones to make your spine more stable. But this will make your back more stiff and may cause arthritis in areas above or below your fused spine.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Many people with spinal stenosis are able to be active with the condition, although they may need to make some changes in their activities or work.
Spine surgery will often partly or fully relieve symptoms in your legs or arms. It is hard to predict if you will improve and how much relief surgery will provide.
- People who had long-term back pain before their surgery are likely to have some pain after surgery.
- If you needed more than one type of back surgery, you may be more likely to have future problems.
- The area of the spinal column above and below a spinal fusion is more likely to be stressed and have problems and accelerated arthritis in the future. This may lead to more surgeries later.
In rare cases, injuries caused by pressure on the nerves are permanent, even if the pressure is relieved.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of spinal stenosis.
More serious symptoms that need prompt attention include:
- Difficulty or poor balance when walking
- Worsening numbness and weakness of your limb
- Problems controlling urine or bowel movements
- Problems urinating or having a bowel movement
References
Bussières A, Cancelliere C, Ammendolia C, et al. Non-surgical interventions for lumbar spinal stenosis leading to neurogenic claudication: a clinical practice guideline. J Pain. 2021;22(9):1015-1039 PMID: 3385761
Gardocki RJ, Park AL. Degenerative disorders of the thoracic and lumbar spine. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 39.
Issac Z, Sarno D. Lumbar spinal stenosis. In: Frontera WR, Silver JK, Rizzo TD Jr, eds. Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 50.
Katz JN, Zimmerman ZE, Mass H, Makhni MC. Diagnosis and management of lumbar spinal stenosis: a review. JAMA. 2022;327(17):1688-1699 PMID: 35503342
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 8/27/2024
Reviewed by: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
