Aneurysm in the brain
Aneurysm - cerebral; Cerebral aneurysm; Aneurysm - intracranial
An aneurysm is a weak area in the wall of a blood vessel that causes the blood vessel to bulge or balloon out. When an aneurysm occurs in a blood vessel of the brain, it is called an intracranial aneurysm. These usually occur around or under the part of the brain called the cerebrum and, when this is true, are called a cerebral aneurysm.
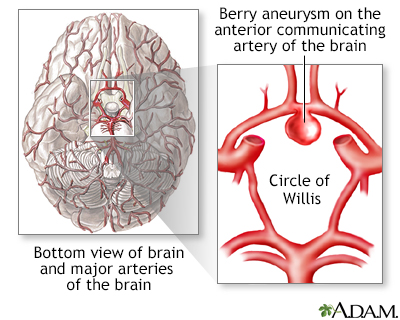
An aneurysm is a sac-like protrusion of an artery caused by a weakened area within the vessel wall. If a cerebral (brain) aneurysm ruptures, the escaping blood within the brain may cause severe neurologic complications or death. A person who has a ruptured cerebral aneurysm may complain of the sudden onset of the worst headache of my life.
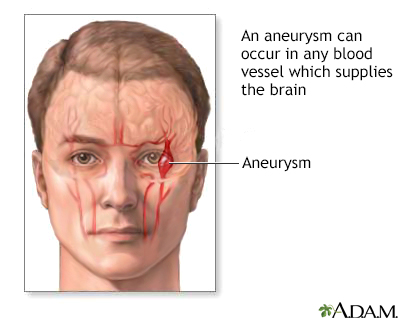
Weakness, numbness, or other loss of nerve function may indicate that an aneurysm may be causing pressure on adjacent brain tissue. Symptoms such as a severe headache, nausea, vomiting, vision changes or other neurological changes can indicate the aneurysm has ruptured and is bleeding into the brain. A ruptured intracranial aneurysm causes intracranial bleeding and is considered very dangerous.
Causes
Aneurysms around the brain occur when there is a weakened area in the wall of a blood vessel. An aneurysm may be present from birth (congenital). Or, it may develop later in life.
There are many types of brain aneurysms. The most common type is called a berry aneurysm. This type can vary in size from a few millimeters (mm) to over a centimeter (cm). Giant berry aneurysms can be bigger than 2.5 cm or 1 inch (in). These are more common in adults. Berry aneurysms, especially when there is more than one, are sometimes passed down through families.
Other types of cerebral aneurysms involve widening of an entire blood vessel (fusiform aneurysms). Aneurysms can occur in any blood vessel that supplies the brain. Hardening of arteries (atherosclerosis), trauma, and infection can all injure the blood vessel wall and cause cerebral aneurysms.
Brain aneurysms are relatively common. One in 50 people has a brain aneurysm, but only a small number of these aneurysms cause symptoms or rupture.
Risk factors include:
- Family history of cerebral aneurysms
- Medical problems such as polycystic kidney disease, coarctation of the aorta, and endocarditis
- High blood pressure, smoking, alcohol, and cocaine, methamphetamine, or amphetamine drug use
Symptoms
A person may have an aneurysm without having any symptoms. This kind of aneurysm may be found when an MRI or CT scan of the brain is done for another reason.
A brain aneurysm may begin to leak a small amount of blood. This may cause a severe headache that a person may describe as "the worst headache of my life." It may be called a thunderclap or sentinel headache. This means the headache could be a warning sign of a future rupture that may occur days to weeks after the headache first started.
Symptoms may also occur if the aneurysm pushes on nearby structures in the brain or breaks open (ruptures) and causes bleeding into the brain.
Symptoms depend on the location of the aneurysm, whether it breaks open, and what part of the brain it is pushing on. Symptoms may include:
- Double vision
- Loss of vision
- Headaches
- Eye pain
- Neck pain
- Stiff neck
- Ringing in the ears
A sudden, severe headache is one symptom of an aneurysm that has ruptured. Other symptoms of an aneurysm rupture may include:
- Confusion, no energy, sleepiness, or stupor
- Eyelid drooping
- Headaches with nausea or vomiting
- Muscle weakness or difficulty moving any part of the body
- Numbness or decreased sensation in any part of the body
- Problems speaking
- Seizures
- Stiff neck (occasionally)
- Vision changes (double vision, loss of vision)
- Loss of consciousness (coma)
NOTE: A ruptured aneurysm is a medical emergency. Call 911 or the local emergency number.
Exams and Tests
An eye exam may show signs of increased pressure in the brain, including swelling of the optic nerve or bleeding into the retina of the eye. A clinical exam may show abnormal eye movement, speech, strength, or sensation.
The following tests may be used to diagnose an intracranial or cerebral aneurysm and determine the cause of bleeding in the brain:
- Cerebral angiography or spiral CT angiogram (CTA) of the head to show the location and size of the aneurysm
- Spinal tap
- CT scan of the head
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- MRI of the head or MRI angiogram (MRA)
Treatment
Two common methods are used to repair a brain aneurysm.
- Clipping is done during open brain surgery (craniotomy).
- Endovascular repair is most often done. It usually involves placing a very small coil and possibly a stent (called coiling and stenting) into or around the aneurysm. This is a less invasive and most common way to treat aneurysms.
Not all aneurysms need to be treated right away. Those that are very small (less than 3 mm or 0.12 in) are less likely to break open.
Your health care provider will help you decide whether or not it is safer to have surgery to block off the aneurysm before it can break open. Sometimes people are too ill to have surgery, or it may be too dangerous to treat the aneurysm because of its location.
A ruptured aneurysm is an emergency that needs to be treated right away. Treatment may involve:
- Being admitted to a hospital's intensive care unit (ICU)
- Complete bed rest and activity restrictions
- Drainage of blood from the brain area (cerebral ventricular drainage)
- Medicines to prevent seizures
- Medicines to control headaches and blood pressure
- Medicines to prevent vasospasm, which is a constriction of the arteries of your brain, leading to decreased blood flow
Once the aneurysm is repaired, treatment may be needed to prevent a stroke from a blood vessel spasm.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do depends on many things. People who are in a deep coma after an aneurysm rupture do not do as well as those with less severe symptoms.
Ruptured cerebral aneurysms are often deadly. Of those who survive, some have no permanent disability. Others have moderate to severe disability.
Possible Complications
Complications of aneurysm in the brain may include:
- Increased pressure inside the skull
- Hydrocephalus, which is caused by an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain
- Loss of movement in one or more parts of the body
- Loss of sensation of any part of the face or body
- Seizures
- Stroke
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (bleeding around the brain)
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (bleeding in the brain)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have a sudden or severe headache, especially if you also have nausea, vomiting, seizures, or any other nervous system symptom.
Also call if you have a headache that is unusual for you, especially if it is severe or your worst headache ever.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent a berry aneurysm from forming. Treating high blood pressure may reduce the chance that an existing aneurysm will rupture. Controlling risk factors for atherosclerosis may reduce the likelihood of some types of aneurysms.
People who are known to have an aneurysm may need regular visits with their provider to make sure the aneurysm is not changing size or shape.
If unruptured aneurysms are discovered in time, they can be treated before causing problems or monitored with regular imaging (usually yearly).
The decision to repair an unruptured cerebral aneurysm is based on the size and location of the aneurysm, and the person's age and general health.
References
American Stroke Association website. What you should know about cerebral aneurysms.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke website. Cerebral aneurysms.
Szeder V, Tateshima S, Jahan R, Saver JL, Duckwiler GR. Intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 67.
Thompson BG, Brown RD Jr, Amin-Hanjani S, et al. Guidelines for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2015:46(8):2368-2400. PMID: 26089327
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 5/10/2024
Reviewed by: Luc Jasmin, MD, Ph.D., FRCS (C), FACS, Department of Neuroscience, Guam Regional Medical City, Guam; Department of Surgery, Johnson City Medical Center, TN; Department of Maxillofacial Surgery at UCSF, San Francisco, CA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
