Coronavirus
Coronavirus - SARS; Coronavirus - 2019-nCoV; Coronavirus - COVID-19; Coronavirus - Severe acute respiratory syndrome; Coronavirus - Middle East respiratory syndrome; Coronavirus - MERS
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses. Infection with these viruses generally causes mild to moderate respiratory illnesses, such as the common cold. Some coronaviruses cause severe illness that can lead to pneumonia, and even death.
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses. Infection with these viruses can cause mild to moderate respiratory illnesses such as the common cold. Some coronaviruses may cause severe illness and lead to pneumonia or even death.
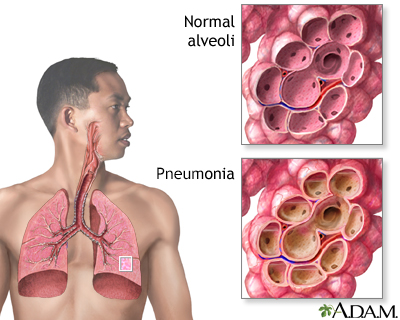
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs caused by an infection. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Pneumonia is a common illness that affects millions of people each year in the United States. The symptoms of pneumonia range from very mild to very severe, even fatal. The severity depends on the type of organism causing pneumonia as well as the age and underlying health of the individual.
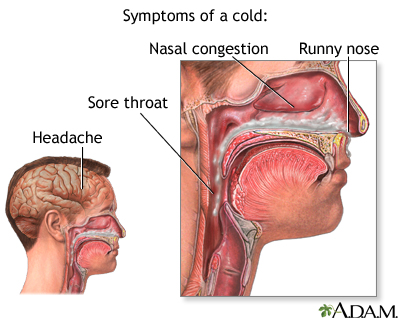
Colds are caused by a virus and can occur year-round. The common cold generally involves a runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. Other symptoms include sore throat, cough, and headache. A cold usually lasts about 7 days, with perhaps a few lingering symptoms such as a cough for another week.
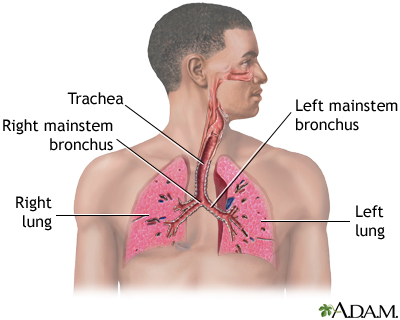
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
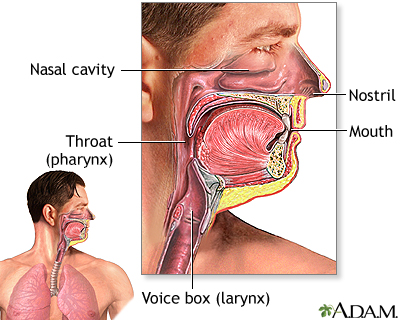
The major passages and structures of the upper respiratory tract include the nose or nostrils, nasal cavity, mouth, throat (pharynx), and voice box (larynx). The respiratory system is lined with a mucous membrane that secretes mucus. The mucus traps smaller particles like pollen or smoke. Hairlike structures called cilia line the mucous membrane and move the particles trapped in the mucus out of the nose. Inhaled air is moistened, warmed, and cleansed by the tissue that lines the nasal cavity.
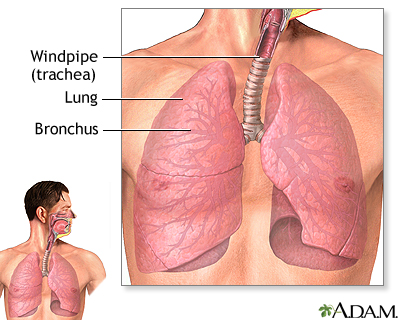
The major passages and structures of the lower respiratory tract include the windpipe (trachea) and within the lungs, the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. Deep in the lungs, each bronchus divides into secondary and tertiary bronchi, which continue to branch to smaller airways called the bronchioles. The bronchioles end in air sacs called the alveoli. Alveoli are bunched together into clusters to form alveolar sacs. Gas exchange occurs on the surface of each alveolus by a network of capillaries carrying blood that has come through veins from other parts of the body.
Causes
There are many different coronaviruses. They affect both humans and animals. Common human coronaviruses cause mild to moderate illnesses, such as the common cold.
Some animal coronaviruses evolve (mutate) and can be passed from animals to humans. They may then spread through person-to-person contact. The coronaviruses that spread from animals to humans can sometimes cause more severe illness:
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a serious form of pneumonia. It is caused by the SARS-CoV coronavirus. No cases in humans have been reported since 2004.
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) is a severe respiratory illness. MERS is caused by the MERS-CoV coronavirus. About 30% of people who have gotten this illness have died. Some people only have mild symptoms. MERS continues to cause illness in humans, mainly in the Arabian Peninsula.
- COVID-19 can be a respiratory illness that causes cold or flu-like symptoms, but it can also affect other parts of your body. It is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). COVID-19 can be a mild to serious illness and even fatal. COVID-19 is a serious public health threat globally and in the United States.
Many coronaviruses originate in bats, which can then infect other animals. SARS-CoV spreads from civet cats, while MERS-CoV spreads from camels. The latest virus, SARS-CoV-2, is also suspected to have originated from animals. It is from the same family of viruses as SARS-CoV, which is why they have similar names. There are many other coronaviruses circulating in animals, but they haven't spread to humans.
Once a person has been infected by a coronavirus, the infection can spread to a healthy person (person-to-person transmission). You can catch coronavirus infection when:
- An infected person sneezes, coughs, or blows their nose near you and releases the virus into the air (droplet infection)
- You touch, hug, shake hands with, or kiss an infected person
Symptoms
Human coronaviruses that cause the common cold spread from person-to-person. Symptoms develop in 2 to 14 days. These include:
- Runny nose
- Sore throat
- Sneezing
- Nasal congestion
- Fever, often with chills
- Headache
- Body aches
- Cough
Exposure to MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 can cause severe symptoms. These include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Diarrhea
- Blood in phlegm (hemoptysis)
- Death
Severe coronavirus infection may cause:
Symptoms may be severe in certain people:
- Children
- Older adults
- People with chronic conditions such as diabetes, cancer, chronic kidney disease, heart disease, or HIV infection
- People with respiratory illnesses such as asthma or COPD
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider may take a sample of the following for lab testing:
- Nasal swab (from the nostrils) or throat swab for a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for SARS-CoV-2 or other viruses
- Blood tests
- Sputum culture
Stool and urine samples may also be taken in some cases.
You may need further testing if your infection is severe. These tests may include:
Diagnostic tests may not be available for all kinds of coronavirus.
Treatment
At this time, there is no specific treatment for coronavirus infection except for SARS-CoV-2. For a coronavirus infection not due to SARS-CoV-2, medicines are given only to ease your symptoms. Experimental treatments are sometimes used in severe cases.
Mild coronavirus infections, such as the common cold, will go away in a few days with rest and self care at home.
If you are suspected to have a severe coronavirus infection and are treated in a hospital, you may:
- Have to wear a face mask
- Stay in an isolated room or ICU for treatment
Treatment for severe infections may include:
- Antibiotics, only if you also have bacterial pneumonia
- Antiviral medicines
- Steroids
- Oxygen, breathing support (mechanical ventilation), or chest therapy
Treatment for COVID-19, the illness due to SARS-CoV-2, may involve additional antiviral medicines.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Common colds due to coronavirus usually resolve on their own. Severe coronavirus infections may require hospitalization and breathing support. Rarely, certain severe coronavirus infections may lead to death, especially in older people, children, or people with chronic conditions.
Possible Complications
Coronavirus infections may lead to bronchitis or pneumonia. Some severe forms may cause organ failure, and even death. Infection with SARS-CoV-2 may lead to long COVID (also called post-acute sequelae of COVID-19) in some people.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have:
- Come in contact with a person with a coronavirus infection
- Travelled to a place which had an outbreak of a coronavirus infection and have developed common cold symptoms, shortness of breath, nausea, or diarrhea
Prevention
Follow these steps to lower your risk of infection:
- Avoid contact with people who have coronavirus infection.
- Avoid travelling to places that have an outbreak of coronavirus infection.
- Wash your hands properly or clean them with an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or sleeve (not your hands) when you sneeze or cough. Throw the tissue away.
- Do not share food, drink, or utensils.
- Clean commonly touched surfaces with a disinfectant.
There are vaccines that can prevent severe disease with COVID-19. Contact your local health department to find out about availability in your area. Information about COVID-19 vaccines is available from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention at
If you are travelling, talk to your provider about:
- Being up-to-date with vaccines
- Taking self-test kits
- Carrying medicines
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. COVID-19: about COVID-19.
Havers FP, Kirking H, Plumb ID. PRE-2019 coronaviruses. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 334.
Perlman S, McIntosh K. Coronaviruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 155.
World Health Organization website. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 1/1/2025
Reviewed by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
