Epididymitis
Epididymitis is swelling (inflammation) of the tube that connects the testicle with the vas deferens. The tube is called the epididymis.
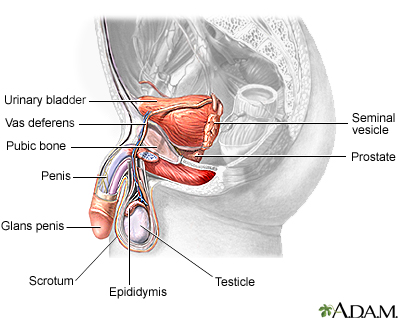
The male reproductive structures include the penis, the scrotum, the testes, the epididymis, the seminal vesicles, and the prostate.
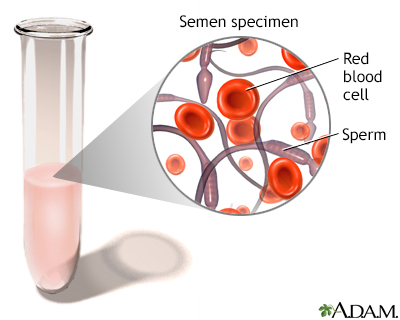
The presence of blood in semen, the fluid discharged upon ejaculation, may be caused by inflammation, infection, obstruction or trauma.
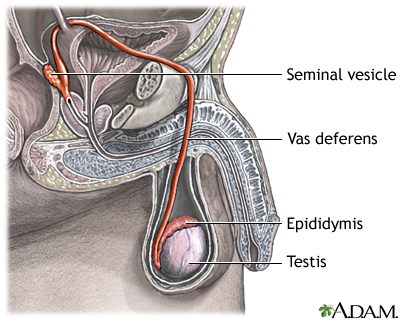
The testes are where sperm are manufactured in the scrotum. The epididymis is a tortuously coiled structure topping the testis, and it receives immature sperm from the testis and stores it for several days. When ejaculation occurs, sperm is forcefully expelled from the tail of the epididymis into the deferent duct. Sperm then travels through the deferent duct through up the spermatic cord into the pelvic cavity, over the ureter to the prostate behind the bladder. Here, the vas deferens joins with the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct, which passes through the prostate and empties into the urethra. When ejaculation occurs, rhythmic muscle movements propel the sperm forward.
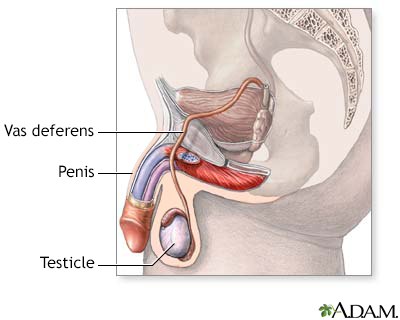
The male reproductive system, viewed from a sagittal section.
Causes
Epididymitis is most common in men ages 19 to 35. It is most often caused by a bacterial infection. Infection often begins in the urethra, the prostate, or the bladder. Gonorrhea and chlamydia infections are most often the cause of the problem in young heterosexual men. In children and older men, it is more commonly caused by E coli and similar bacteria. This is also true in men who have sex with men.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) can cause epididymitis. Other bacteria (such as Ureaplasma) may also cause the condition.
Amiodarone is a medicine which prevents abnormal heart rhythms. This medicine can also cause epididymitis.
The following increase the risk for epididymitis:
- Recent surgery
- Past structural problems in the urinary tract
- Regular use of a urethral catheter
- Sexual intercourse with more than one partner and not using condoms
- Enlarged prostate
Symptoms
Epididymitis may begin with:
- Low fever
- Chills
- Feeling of heaviness in the testicle area
The testicle area will get more sensitive to pressure. It will become painful as the condition progresses. An infection in the epididymis can easily spread to the testicle.
Other symptoms include:
- Blood in the semen
- Discharge from the urethra (the opening at the end of the penis)
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvis
- Lump near the testicle
Less common symptoms are:
- Pain during ejaculation
- Pain or burning during urination
- Painful scrotal swelling (epididymis is enlarged)
- Tender, swollen, and painful groin area on affected side
- Testicle pain that gets worse during a bowel movement
Symptoms of epididymitis may be similar to those of testicular torsion, which requires emergent treatment.
Exams and Tests
Physical exam will show a red, tender lump on the affected side of the scrotum. You may have tenderness in a small area of the testicle where the epididymis is attached. A large area of swelling may develop around the lump.
The lymph nodes in the groin area may be enlarged. There may also be discharge from the penis. A rectal exam may show an enlarged or tender prostate.
These tests may be performed:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Doppler ultrasound
- Testicular scan (nuclear medicine scan)
- Urinalysis and culture (you may need to give several specimens, including initial stream, mid-stream, and after a prostate massage)
- Tests for chlamydia and gonorrhea
Treatment
Your health care provider will prescribe medicine to treat the infection. Sexually transmitted infections need antibiotics. Your sexual partners should also be treated. You may need pain medicines and anti-inflammatory medicines.
If you are taking amiodarone, you may need to lower your dose or change your medicine. Talk with your provider.
To ease discomfort:
- Rest lying down with the scrotum elevated.
- Apply ice packs to the painful area (but do not apply ice directly to the area).
- Wear underwear with more support or an athletic supporter.
You will need to follow-up with your provider to make sure the infection has cleared completely.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Epididymitis most often gets better with antibiotic treatment. There are no long-term sexual or reproductive problems in most cases. However, the condition may return.
Possible Complications
Complications include:
- Abscess in the scrotum
- Long-term (chronic) epididymitis
- Opening on the skin of the scrotum
- Death of testicular tissue due to lack of blood (testicular infarction)
- Infertility
Sudden and severe pain in the scrotum is a medical emergency. You need to be seen by a provider right away.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of epididymitis. Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have sudden, severe testicle pain or pain after an injury.
Prevention
You can prevent complications if you get diagnosed and treated early.
Your provider may prescribe antibiotics before a surgery. This is because some surgeries could raise the risk for epididymitis. Practice safe sex. Avoid multiple sexual partners and use condoms. This may help prevent epididymitis caused by sexually transmitted diseases.
References
Pontari M. Inflammatory and pain conditions of the male genitourinary tract: prostatitis and related pain conditions, orchitis, and epididymitis. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 56.
Reno HEL, Geisler WM. Diseases caused by chlamydiae. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 294.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 9/2/2024
Reviewed by: Kelly L. Stratton, MD, FACS, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
