Hyperaldosteronism - primary and secondary
Conn syndrome; Mineralocorticoid excess
Hyperaldosteronism is a disorder in which the adrenal gland releases too much of the hormone aldosterone into the blood.
Hyperaldosteronism can be primary or secondary.
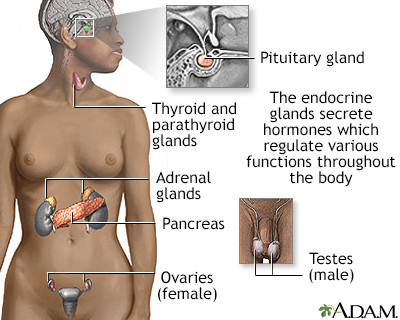
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the pace of chemical activity in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
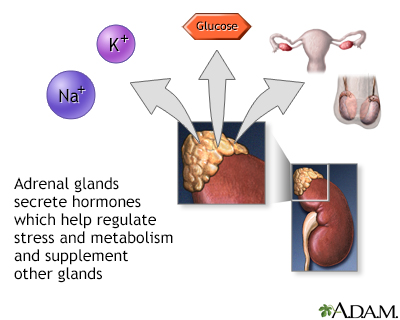
Adrenal glands produce hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, steroids, cortisol, and cortisone, and chemicals such as adrenalin (epinephrine), norepinephrine, and dopamine. When the glands produce more or less hormones than required by the body, disease conditions may occur.
Causes
Hyperaldosteronism occurs when the adrenal glands release too much aldosterone.
Primary hyperaldosteronism is due to a problem of the adrenal glands themselves. Most cases are caused by a noncancerous (benign) tumor of the adrenal gland.
Secondary hyperaldosteronism is due to a problem elsewhere in the body that causes the adrenal glands to release too much aldosterone. These problems can be with:
- Genes
- Diet
- Medical disorders such as with the heart, liver, kidneys, or high blood pressure
The condition mostly affects people 30 to 50 years old and is a common cause of high blood pressure in middle age.
Symptoms
Primary and secondary hyperaldosteronism have common symptoms, including:
- High blood pressure
- Low level of potassium in the blood
- Feeling tired all the time
- Headache
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms.
Tests that may be ordered to diagnose hyperaldosteronism include:
- Abdominal CT scan
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Blood aldosterone level
- Blood renin activity
- Blood potassium level
- Urinary aldosterone
- Kidney ultrasound
Sometimes blood and urine tests may be done after eating a high salt diet or after receiving saline through a vein (intravenous). You may need to stop taking some medicines before the tests. Your provider will tell you what to do before the procedure.
Another procedure involves inserting a catheter into the veins of the adrenal glands. This helps check which of the two adrenal glands is making too much aldosterone. This test is important because many people have small benign tumors in the adrenal glands that do not secrete any hormones. Relying only on a CT scan may result in the wrong adrenal gland being removed.
Treatment
Primary hyperaldosteronism caused by an adrenal gland tumor is often treated with surgery. It can sometimes be treated with medicines.
Removing the adrenal tumor may control the symptoms. Even after surgery, some people still have high blood pressure and need to take medicine. But often, the number of medicines or doses can be lowered.
Limiting salt intake and taking medicine may control the symptoms without surgery. Medicines to treat hyperaldosteronism include:
- Medicines that block the action of aldosterone
- Water pills (diuretics), which help manage fluid buildup in the body
Secondary hyperaldosteronism is treated with medicines (as described above) and limiting salt intake. Surgery is usually not used.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook for primary hyperaldosteronism is good with early diagnosis and treatment.
The outlook for secondary hyperaldosteronism depends on the cause of the condition.
Possible Complications
Primary hyperaldosteronism can cause very high blood pressure, which can damage many organs, including the eyes, kidneys, heart, and brain.
Erection problems and enlarged breast tissue in men (gynecomastia) may occur with long-term use of medicines to block the effect of hyperaldosteronism.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider for an appointment if you develop symptoms of hyperaldosteronism.
References
Nieman LK. Adrenal cortex. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 208.
Young WF. Endocrine hypertension. In. Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 16.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 7/30/2023
Reviewed by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
