Rheumatoid arthritis
RA; Arthritis - rheumatoid
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It is a long-term disease. It can also affect other organs.

Most of us expect to become a little achy and creaky as we get older. It's because the cushion that protects our joints wears down over the years, a condition called osteoarthritis. But some people develop a form of arthritis at an earlier age, not because their joints are wearing away, but because their body is attacking and damaging their own joints. Let's talk about rheumatoid arthritis, or RA. The immune system normally keeps the body safe against bacteria, viruses, and other harmful invaders. But sometimes this system goes a little haywire, and the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues. That's known as an autoimmune disease. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks and damages your own joints. Like other forms of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis makes the joints painful and stiff. If you have RA, you may notice that your joints feel stiffer in the morning, making it hard to get out of bed. Over time, you'll have trouble moving the affected joints, which can become deformed and bent out of shape. So, how do doctors diagnose rheumatoid arthritis? Well, there isn't one test that can tell for sure that you have RA. However, there are a couple of lab tests that can point your doctor to the diagnosis. You may also have an ultrasound, MRI, or x-rays so your doctor can see what's going on inside the affected joints. If you do have RA, many drugs can treat it. However, each of these drugs can have some side effects, and some of them are serious. You'll have to decide with your doctor which drug to take by weighing the benefits against the risks. If you're like most people with RA, you'll start by taking medicines called disease modifying antirheumatic drugs, or DMARDs for short. These include methotrexate. Often antimalarial drugs are given along with DMARDs. Anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib can help bring down the swelling in your joints. So can steroid drugs. If these medicines don't work, your doctor may suggest trying a biologic medicine, which targets the overactive immune response that's damaging your joints. Biologics are usually injected under the skin or into a vein. Severely deformed joints may need to be treated with surgery to remove the joint lining or even totally replace the damaged joint. Whatever treatment you use, also remember to exercise your joints on your own, or by going to a physical therapist. The right exercise can help keep your muscles strong and improve your joint mobility. When you have RA, don't try to overdo it. Think about your achy joints before doing any activity, so you don't overstress them. Also follow your doctor's treatment advice carefully. If you let this disease go, you could end up with permanent joint damage that can't be reversed. By treating RA early, you can get your joints, and the rest of you, moving more smoothly again.
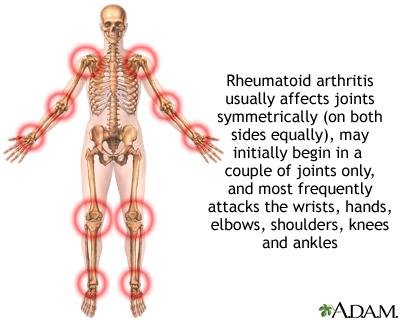
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks itself. The pattern of joints affected is usually symmetrical, involves the hands and other joints and is worse in the morning. Rheumatoid arthritis is also a systemic disease, involving other body organs, whereas osteoarthritis is limited to the joints. Over time, both forms of arthritis can be crippling.
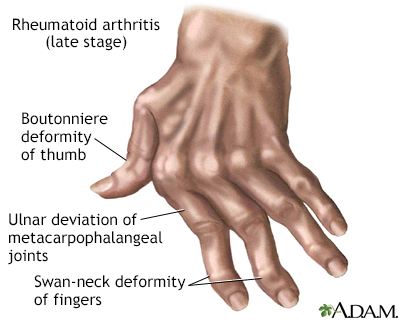
The affect of rheumatoid arthritis can progress to the degree that it is crippling. Deformities distinctive to late-stage rheumatoid arthritis such as ulnar deviation of the bones of the hands, or swan-neck deviation of the fingers occur because muscles and tendons on one side of the joint may overpower those on the other side, pulling the bones out of alignment.
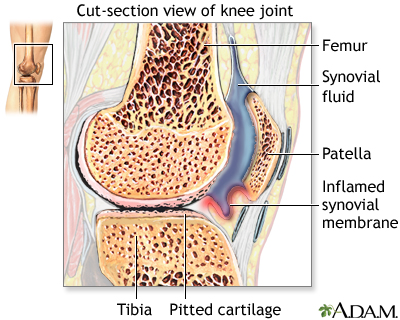
Rheumatoid arthritis is another form of arthritis. The body's own immune system attacks a joint's synovial membrane, which secretes fluid and lines the joint. The synovium becomes inflamed, produces excess fluid, and the cartilage becomes rough and pitted.
Causes
The cause of RA is not known. It is an autoimmune disease. This means the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
RA can occur at any age, but is more common in middle age. Women get RA more often than men.
Infection, genes, and hormone changes may be linked to the disease. Smoking may also be linked to RA.
It is less common than osteoarthritis (OA) which is a joint condition that occurs in many people due to wear and tear on the joints as they age.
Symptoms
Most of the time, RA affects joints on both sides of the body equally. Fingers, wrists, knees, feet, elbows, ankles, hips and shoulders are the most commonly affected. The lower spine is usually not affected by RA.
The disease often begins slowly. Early symptoms may include:
- Minor joint pain
- Stiffness
- Fatigue
Joint symptoms may include:
- Morning stiffness, which lasts more than 1 hour, is common.
- Joints may feel warm, tender, and stiff when not used for an hour.
- Joint pain is often felt in the same joint on both sides of the body.
- Joints are often swollen.
- Over time, joints may lose their range of motion and may become deformed.
Other symptoms include:
- Chest pain when taking a breath (pleurisy)
- Dry eyes and mouth (Sjögren syndrome)
- Eye burning, itching, and discharge
- Nodules under the skin (most often a sign of more severe disease)
- Numbness, tingling, or burning in the hands and feet
- Sleep difficulties
The diagnosis of RA is made when:
- You have pain and swelling in 3 or more joints.
- Arthritis has been present for longer than 6 weeks.
- You have a positive test for rheumatoid factor or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody.
- You have an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
- Other types of arthritis have been ruled out.
Sometimes the diagnosis of RA is made even without all of the conditions shown above if the arthritis is otherwise typical for RA.
Exams and Tests
There is no test that can determine for sure whether you have RA. Most people with RA will have some abnormal test results. However, some people will have normal results for all tests.
Two lab tests that are positive in most people and often help in the diagnosis are:
- Rheumatoid factor
- Anti-CCP antibody
These tests are positive in most patients with RA. The anti-CCP antibody test is more specific for RA.
Other tests that may be done include:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Metabolic panel and serum uric acid
- CRP
- ESR
- Antinuclear antibody
- Tests for hepatitis
- Joint x-rays
- Joint ultrasound or MRI
- Joint fluid analysis
Treatment
RA most often requires long-term treatment by an expert in arthritis called a rheumatologist. Treatment includes:
- Medicines
- Physical therapy
- Exercise
- Education to help you understand the nature of RA, your treatment options, and the need for regular follow-up.
- Surgery, if required
Early treatment for RA with medicines called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) should be used in all patients. This will slow joint destruction and prevent deformities. The activity of the RA should be checked at regular visits to make sure the disease is under control. The goal of treatment is to stop the progression of the RA.
MEDICINES
Anti-inflammatory medicines: These include aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, naproxen and celecoxib.
- These medicines work very well to reduce joint swelling and inflammation, but they can have long-term side effects. Therefore, they should be taken only for a short time and in low doses when possible.
- Since they do not prevent joint damage if used alone, DMARDs should be used as well.
Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These are often the medicines that are tried first in people with RA. They are prescribed along with rest, strengthening exercise, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Methotrexate is the most commonly used DMARD for RA. Leflunomide and hydroxychloroquine may also be used.
- Sulfasalazine is a medicine that is often combined with methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine (triple therapy).
- It may be weeks or months before you see any benefit from these medicines.
- These medicines may have serious side effects, so you will need frequent blood tests and other monitoring when taking them.
- Antimalarial medicines -- This group of medicines includes hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil). They are most often used along with methotrexate. It may be weeks or months before you see any benefit from these medicines.
Corticosteroids -- These medicines work very well to reduce joint swelling and inflammation, but they can have long-term side effects and do not prevent joint damage if used alone. Therefore, they should be taken only for a short time and in low doses when possible.
Biologic DMARD agents -- These medicines are designed to affect parts of the immune system that play a role in the disease process of RA.
- They may be given when other medicines, usually methotrexate, have not worked. Biologic medicines are often added to methotrexate. However, because they are very expensive, insurance approval is generally required.
- Most of them are given either under the skin or into a vein. There are now many different types of biologic agents.
Biologic and synthetic agents can be very helpful in treating RA. However, people taking these medicines must be watched closely because of uncommon, but serious adverse reactions:
- Infections from bacteria, viruses, and fungi
- Skin cancer, but not melanoma
- Skin reactions
- Allergic reactions
- Worsened heart failure
- Damage to nerves
- Low white blood cell count
SURGERY
Surgery may be needed to correct severely damaged joints. Surgery may include:
- Removal of the joint lining (synovectomy)
- Total joint replacement, in extreme cases, may include total knee replacement (TKR) and hip replacement.
PHYSICAL THERAPY
Range-of-motion exercises and exercise programs prescribed by a physical therapist can delay the loss of joint function and help keep muscles strong.
Sometimes, therapists will use special machines to apply deep heat or electrical stimulation to reduce pain and improve joint movement.
Other therapies that may help ease joint pain include:
- Joint protection techniques
- Heat and cold treatments
- Splints or orthotic devices to support and align joints
- Frequent rest periods between activities, as well as 8 to 10 hours of sleep per night
NUTRITION
Some people with RA may have intolerance or allergies to certain foods. A balanced nutritious diet is recommended. It may be helpful to eat foods rich in fish oils (omega-3 fatty acids). Smoking cigarettes should be stopped. Excessive alcohol should also be avoided.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with RA and their families can be found by taking part in an arthritis support group.
Some people may benefit from taking part in an arthritis support group.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Whether your RA progresses or not depends on the severity of your symptoms and your response to treatment. It is important to start the treatment as soon as possible. Regular follow up visits with a rheumatologist are needed to adjust the treatment.
Permanent joint damage may occur without proper treatment. Early treatment with a three-medicine DMARD combination known as "triple therapy," or with biologic or targeted synthetic medicines can prevent joint pain and damage.
Possible Complications
If not well treated, RA can affect nearly every part of the body. Complications may include:
- Damage to the lung tissue.
- Increased risk of hardening of the arteries, leading to cardiovascular disease.
- Spinal injury when the neck bones become damaged.
- Inflammation of the blood vessels (rheumatoid vasculitis), which can lead to skin, nerve, heart, and brain problems.
- Swelling and inflammation of the outer lining of the heart (pericarditis) and of the heart muscle (myocarditis), which can lead to congestive heart failure.
However, these complications can be avoided with proper treatment. The treatments for RA can also cause serious side effects. Talk to your provider about the possible side effects of treatment and what to do if they occur.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you think you have symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Prevention
There is no known prevention. Smoking appears to worsen RA, so it is important to avoid tobacco. Proper early treatment can help prevent further joint damage.
References
England BR, O'Dell JR. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Firestein GS, McInnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 73.
Fraenkel L, Bathon JM, England BR, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021;73(7):924-939. PMID: 34101387
McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 243.
Melville AR, Buch MH. Management of rheumatoid arthritis in DMARD-naïve patients. In: Hochberg MC, Gravallese EM, Smolen JS, van der Hejjde D, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH, eds. Rheumatology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 100.
Mori S, Urata Y, Yoshitama T, Ueki Y. Tofacitinib versus tocilizumab in the treatment of biological-naïve or previous biological-failure patients with methotrexate-refractory active rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. 2021;7(2):e001601. PMID: 33958440
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 1/25/2023
Reviewed by: Neil J. Gonter, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Columbia University, NY and private practice specializing in Rheumatology at Rheumatology Associates of North Jersey, Teaneck, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Internal review and update on 07/12/2024 by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
