Bleeding
Blood loss; Open injury bleeding
Bleeding is the loss of blood. Bleeding may be:
- Inside the body (internal)
- Outside the body (external)
Bleeding may occur:
- Inside the body when blood leaks from blood vessels or organs
- Outside the body when blood flows through a natural opening (such as the ear, nose, mouth, vagina, or rectum)
- Outside the body when blood moves through a break in the skin
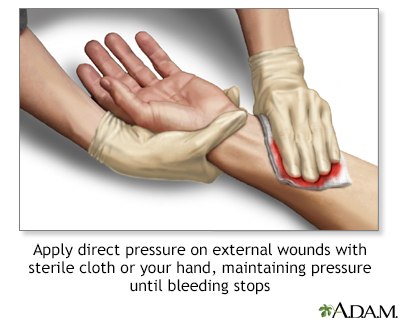
Bleeding from most injuries can be stopped by applying direct pressure to the injury. This keeps from cutting off the blood supply to the affected limb.
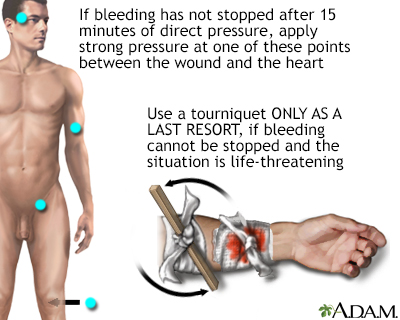
When there is severe bleeding where a major artery has been severed, pressure may be insufficient and a tourniquet may be necessary. Tourniquets are an effective way of stopping bleeding from an extremity. They do, however, stop circulation to the affected extremity and should ONLY be used when other methods, such as pressure dressings, have failed (or are likely to fail). Pressure from tourniquets must be relieved periodically to prevent damage to the tissue from lack of oxygen.

Bleeding from most injuries can be stopped by applying direct pressure to the injury. This keeps from cutting off the blood supply to the affected limb. When there is severe bleeding, where a major artery has been severed, pressure may be insufficient and a tourniquet may be necessary.
Considerations
Get emergency medical help for severe bleeding. This is very important if you think there is internal bleeding. Internal bleeding can very quickly become life threatening. Immediate medical care is needed.
Serious injuries may cause heavy bleeding. Sometimes, minor injuries can bleed a lot. An example is a scalp wound.
You may bleed a lot if you take blood-thinning medicine or have a bleeding disorder such as hemophilia. Bleeding in such people requires medical attention right away.
The most important step for external bleeding is to apply direct pressure. This will likely stop most external bleeding.
Always wash your hands before (if possible) and after giving first aid to someone who is bleeding. This helps prevent infection.
Try to use latex gloves when treating someone who is bleeding. Latex gloves should be in every first aid kit. People allergic to latex can use nonlatex gloves. You can catch infections, such as viral hepatitis or HIV/AIDS, if you touch infected blood and it gets into an open wound, even a small one.
Although puncture wounds usually don't bleed very much, they carry a higher risk for infection. Seek medical care to prevent tetanus or other infection.
Abdominal, pelvic, groin, neck, and chest wounds can be very serious because of the possibility of severe internal bleeding. They may not look very serious, but can result in shock and death.
- Seek medical care right away for any abdominal, pelvic, groin, neck, or chest wound.
- If organs are showing through the wound, do not try to push them back into place.
- Cover the injury with a moist cloth or bandage.
- Apply gentle pressure to stop the bleeding in these areas.
Blood loss can cause blood to collect under the skin, turning it black and blue (bruised). Apply a cool compress to the area as soon as possible to reduce swelling. Do not place ice directly on the skin. Wrap the ice in a towel first.
Causes
Bleeding can be caused by injuries, or it can be spontaneous. Spontaneous bleeding most commonly occurs with problems in the joints, or gastrointestinal or urogenital tracts.
Symptoms
You may have symptoms such as:
- Blood coming from an open wound
- Bruising
Bleeding can also cause shock, which may include any of the following symptoms:
- Confusion or decreasing alertness
- Clammy skin
- Dizziness or light headedness after an injury
- Low blood pressure
- Paleness (pallor)
- Rapid pulse (increased heart rate)
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
Symptoms of internal bleeding may include those listed above for shock as well as the following:
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Chest pain
- Skin color changes
Blood coming from a natural opening in the body may also be a sign of internal bleeding. These symptoms include:
- Blood in the stool (appears black, maroon, or bright red)
- Blood in the urine (appears red, pink, or tea-colored)
- Blood in the vomit (looks bright red, or brown like coffee-grounds)
- Vaginal bleeding (heavier than usual or after menopause)
First Aid
First aid is appropriate for external bleeding. If bleeding is severe, or if you think there is internal bleeding, or the person is in shock, get emergency help.
- Calm and reassure the person. The sight of blood can be very frightening.
- If the wound affects just the top layers of skin (superficial), wash it with soap and warm water and pat dry. Bleeding from superficial wounds or scrapes (abrasions) is often described as oozing, because it is slow.
- Lay the person down. This reduces the chances of fainting by increasing blood flow to the brain. When possible, raise up the part of the body that is bleeding.
- Remove any loose debris or dirt that you can see from a wound.
- Do not remove an object such as a knife, stick, or arrow that is stuck in the body. Doing so may cause more damage and bleeding. Place pads and bandages around the object and tape the object in place.
- Put pressure directly on an external wound with a sterile bandage, clean cloth, or even a piece of clothing. If nothing else is available, use your hand. Direct pressure is best for external bleeding, except for an eye injury.
- Maintain pressure until the bleeding stops. When it has stopped, tightly wrap the wound dressing with adhesive tape or a piece of clean clothing. Do not peek to see if the bleeding has stopped.
- If bleeding continues and seeps through the material being held on the wound, do not remove it. Simply place another cloth over the first one. Be sure to seek medical attention right away.
- If the bleeding is severe, get medical help right away and take steps to prevent shock. Keep the injured body part completely still. Lay the person flat, raise the feet about 12 inches (in) or 30 centimeters (cm), and cover the person with a coat or blanket. If possible, do not move the person if there has been a head, neck, back, or leg injury, as doing so may make the injury worse. Get medical help as soon as possible.
WHEN TO USE A TOURNIQUET
If continuous pressure has not stopped the bleeding, and bleeding is extremely severe (life threatening), a tourniquet can be used until medical help arrives.
- The tourniquet should be applied to the limb 2 to 3 in (5 to 7.5 cm) above the bleeding wound. Avoid the joint. If needed, place the tourniquet above the joint, toward the torso.
- If possible, do not apply the tourniquet directly on the skin. Doing so may twist or pinch the skin and tissues. Use padding or apply the tourniquet over the pant leg or sleeve.
- If you have a first-aid kit that comes with a tourniquet, apply it to the limb.
- If you need to make a tourniquet, use bandages 2 to 4 in (5 to 10 cm) wide and wrap them around the limb several times. Tie a half or square knot, leaving loose ends long enough to tie another knot. A stick or a stiff rod should be placed between the two knots. Twist the stick until the bandage is tight enough to stop the bleeding and then secure it in place.
- If at all possible, always write down the time when the tourniquet was applied. If this is not possible, then you must remember the time. Tell this to medical responders. (Keeping a tourniquet on for too long can injure the nerves and tissues.)
Do Not
Do not peek at a wound to see if the bleeding is stopping. The less a wound is disturbed, the more likely it is that you will be able to control the bleeding.
Do not probe a wound or pull out any embedded object from a wound. This will usually cause more bleeding and harm.
Do not remove a dressing if it becomes soaked with blood. Instead, add a new one on top.
Do not try to clean a large wound. This can cause heavier bleeding.
Do not try to clean a wound after you get the bleeding under control. Get medical help.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek medical help right away if:
- Bleeding can't be controlled, it required the use of a tourniquet, or it was caused by a serious injury.
- The wound might need stitches.
- Gravel or dirt can't be removed easily with gentle cleaning.
- You think there may be internal bleeding or shock.
- Signs of infection develop, including increased pain, redness, swelling, yellow or brown fluid, swollen lymph nodes, fever, or red streaks spreading from the site toward the heart.
- The injury was due to an animal or human bite.
- The person has not had a tetanus shot in the last 5 to 10 years.
Prevention
Use good judgment and keep knives and sharp objects away from small children.
Stay up-to-date on vaccinations.
References
Bulger EM, Snyder D, Schoelles K, et al. An evidence-based prehospital guideline for external hemorrhage control: American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2014;18(2):163-173. PMID: 24641269
Hayward CPM, Ma AD. Evaluation of the patient with suspected bleeding disorders. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 126.
Qasim Z. Prehospital management of the trauma patient. In: Cameron JL, Cameron AM, eds. Current Surgical Therapy. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:1224-1230.
Simon BC, Hern HG. Wound management principles. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 50.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 11/2/2023
Reviewed by: Jesse Borke, MD, CPE, FAAEM, FACEP, Attending Physician at Kaiser Permanente, Orange County, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
