Aging changes in immunity
Your immune system helps protect your body from foreign or harmful substances. Examples are bacteria, viruses, toxins, cancer cells, and blood or tissues from another person. The immune system makes cells and antibodies that destroy these harmful substances.
AGING CHANGES AND THEIR EFFECTS ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
As you grow older, your immune system does not work as well. The following immune system changes may occur:
- The immune system becomes slower to respond. This increases your risk of getting sick. Flu shots or other vaccines may not work as well or protect you for as long as expected.
- An autoimmune disorder may develop. This is a disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages or destroys healthy body tissues.
- Your body may heal more slowly. There are fewer immune cells in the body to bring about healing.
- The immune system's ability to detect and correct cell defects also declines. This can result in an increased risk of cancer.
PREVENTION
To decrease the risks from immune system aging:
- Get vaccines to prevent the flu, COVID-19, shingles, and pneumococcal infections, as well as any other vaccines your health care provider recommends.
- Get plenty of exercise. Exercise helps boost your immune system.
- Eat healthy foods. Good nutrition keeps your immune system strong.
- Do not smoke. Smoking weakens your immune system.
- Limit your intake of alcohol. Ask your provider how much alcohol is safe for you.
- Look into safety measures to prevent falls and injuries. A weak immune system can slow healing from injuries.
OTHER CHANGES
As you grow older, you will have other changes, including in your:
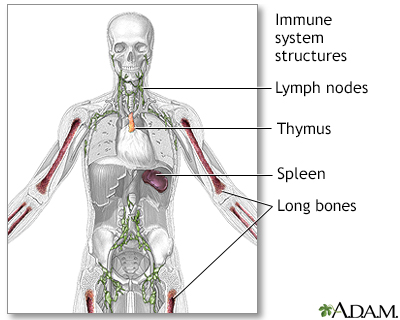
The immune system protects the body from potentially harmful substances. The inflammatory response (inflammation) is part of innate immunity. It occurs when tissues are injured by bacteria, trauma, toxins, heat, or any other cause.
References
McDevitt MA. Aging and the blood. In: Fillit HM, Rockwood K, Young J, eds. Brocklehurst's Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 24.
Tummala MK, Taub DD, Ershler WB. Clinical immunology: immune senescence and the acquired immunodeficiency of aging. In: Fillit HM, Rockwood K, Young J, eds. Brocklehurst's Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 93.
Walston JD. Common clinical sequelae of aging. In: Goldman L, Cooney CA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 24.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 7/15/2024
Reviewed by: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
