Aging changes in the breast
With age, a woman's breasts lose fat, tissue, and mammary glands. Many of these changes are due to the decrease in the body's production of estrogen that occurs at menopause. Without estrogen, the gland tissue shrinks, making the breasts smaller and less full. The connective tissue that supports the breasts becomes less elastic, so the breasts sag.
Changes also occur in the nipple. The area surrounding the nipple (the areola) becomes smaller and may nearly disappear. The nipple may also turn in slightly.
Breast lumps are common around the time of menopause. These are usually noncancerous cysts. However, if you notice a lump, make an appointment with your health care provider, because breast cancer risk increases with age. Women should be aware of the benefits and limitations of breast self-exams. These exams do not always pick up early stages of breast cancer. Women should talk to their providers about regular physical examinations and mammograms or other imaging to screen for breast cancer.
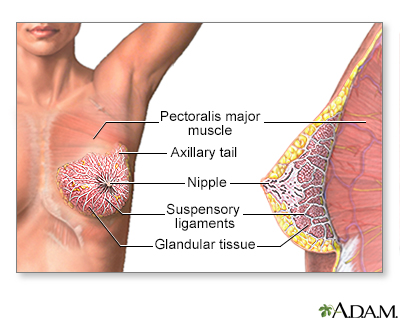
The female breast is either of two mammary glands (organs of milk secretion) on the chest.
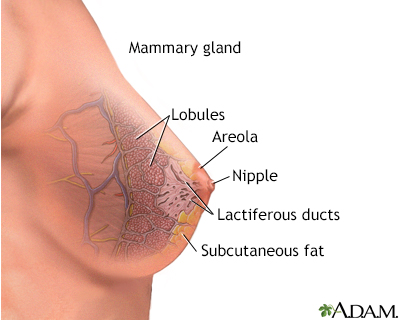
The anatomy of the breast includes the lactiferous, or milk ducts, and the mammary lobules.
References
Davidson NE. Breast cancer and benign breast disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 183.
Lobo RA, Suh Y. Menopause and aging. In: Strauss JF III, Barbieri R, Dokras A, Williams CJ, Williams Z, eds. Yen & Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 14.
Walston JD. Common clinical sequelae of aging. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 24.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 7/15/2024
Reviewed by: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
