Autoinoculation
Autoinoculation is a procedure in which cells are removed from the body, treated or medically changed, and then placed back into the body. It is done to help prevent an immune reaction or to help diagnose a medical condition or illness.
Autoinoculation can also refer to the movement of microorganisms from one part of the body to another.
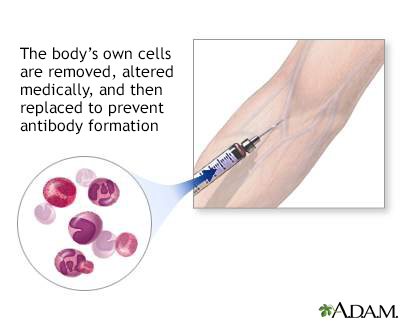
Injection of some of the body's cells back into the body is called autoinoculation. Using one's own cells helps prevent or reduce antibody formation.
References
Merriam-Webster's Medical Dictionary. Autoinoculation.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 7/23/2024
Reviewed by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
