Malignancy
The term malignancy refers to the presence of cancerous cells that have the ability to spread to other sites in the body (metastasize) or to invade nearby (locally) and destroy tissues. Malignant cells tend to have fast, uncontrolled growth and do not die normally due to changes in their genetic makeup.
Malignant cells that are resistant to treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, may return after all detectable traces of them have been removed or destroyed.
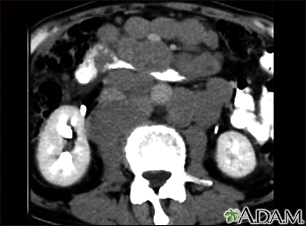
This abdominal CT scan shows tumor masses (malignant lymphomas) in the area behind the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal space).
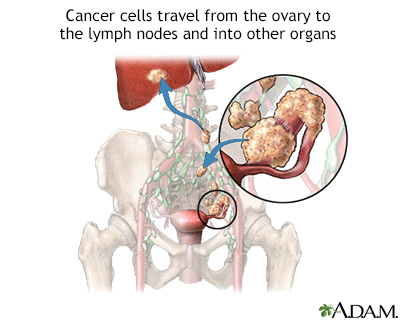
Malignancy refers to cells that are cancerous. Malignant cells may spread from their primary cancer source. This is called metastatic cancer.
References
National Cancer Institute website. NCI dictionary of cancer terms.
Park BH. Cancer biology and genetics. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 166.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 8/21/2024
Reviewed by: Warren Brenner, MD, Oncologist, Lynn Cancer Institute, Boca Raton, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
