Diskectomy
Spinal microdiskectomy; Microdecompression; Laminotomy; Disk removal; Spine surgery - diskectomy; Discectomy
Diskectomy is surgery to remove all or part of the cartilage cushion that helps support part of your spinal column. These cushions are called disks, and they separate your spinal bones (vertebrae).
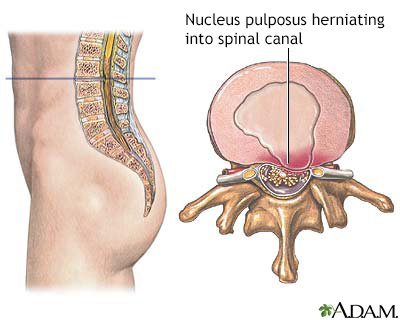
Herniated nucleus pulposus is a condition in which part or all of the soft, gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk is forced through a weakened part of the disk, resulting in back pain and nerve root irritation.
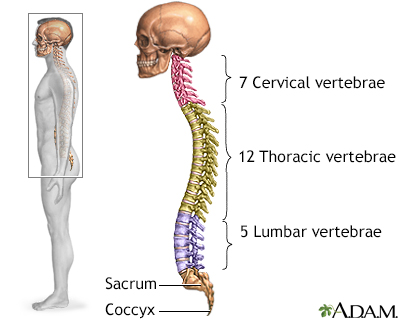
The spine is divided into several sections. The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. The thoracic vertebrae comprise the chest section and have ribs attached. The lumbar vertebrae are the remaining vertebrae below the last thoracic bone and the top of the sacrum. The sacral vertebrae are caged within the bones of the pelvis, and the coccyx represents the terminal vertebrae or vestigial tail.
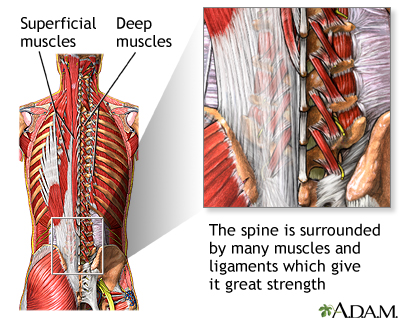
The spine is surrounded by many muscles and ligaments which give it great strength and flexibility. If these muscles or ligaments become damaged, back pain results.
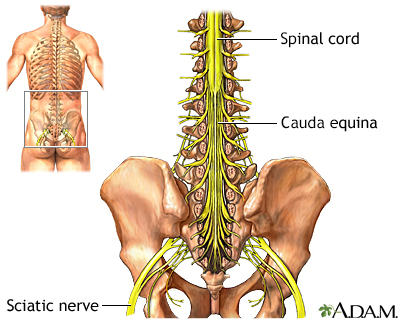
The spinal cord ends in the lumbar area and continues through the vertebral canal as spinal nerves. Because of its resemblance to a horses tail, the collection of these nerves at the end of the spinal cord is called the cauda equina. These nerves send and receive messages to and from the lower limbs and pelvic organs.
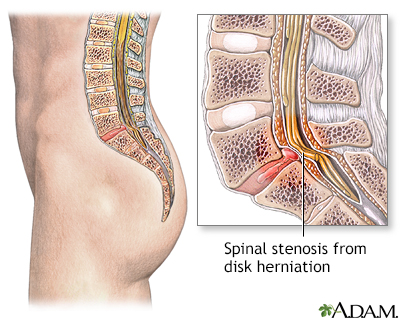
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the lumbar or cervical spinal canal. The narrowing can cause compression on nerve roots resulting in pain or weakness of the legs. Medications or steroid injections are often administered to reduce inflammation. If the pain is persistent and does not respond to these conservative measures, surgery is considered to relieve the pressure on the nerves.
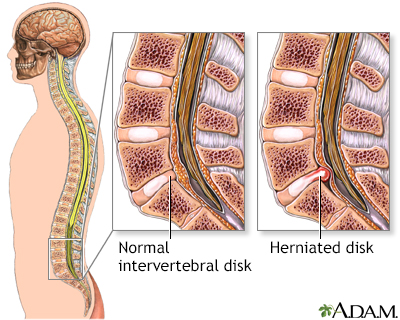
The appearance of a normal intervertebral disk is compared to a herniated disk.
Description
Your surgeon may perform disk removal (diskectomy) in these different ways.
- Microdiskectomy: When you have a microdiskectomy, your surgeon does not need to do much surgery on the bones, joints, ligaments, or muscles of your spine.
- Diskectomy in the lower part of your back (lumbar spine) may be part of a larger surgery that also includes a laminectomy, foraminotomy, or spinal fusion.
- Diskectomy in your neck (cervical spine) is most often done along with foraminotomy, or fusion.
Microdiskectomy is done in a hospital or outpatient surgical center. You will be given general anesthesia. You will be asleep and pain-free.
- Your surgeon makes a small (1 to 1.5-inch, or 2.5 to 3.8-centimeter) incision (cut) on your back and moves the back muscles away from your spine. Your surgeon uses a special microscope to see the problem disk or disks and nerves during surgery.
- The nerve root is located and gently moved away.
- Your surgeon removes the injured disk tissue and pieces of the disk.
- The back muscles are returned to their normal place.
- The incision is closed with stitches or staples.
- The surgery takes about 1 to 2 hours.
Diskectomy and laminotomy are usually done in a hospital or outpatient surgical center, using general anesthesia (asleep and pain-free).
- Your surgeon makes a larger cut on your back over the spine.
- Muscles and other tissues are gently moved to expose your spine.
- A small part of the lamina bone (part of the vertebrae that surrounds the spinal column and nerves) is cut away. The opening may be as large as the ligament that runs along your spine.
- A small hole is cut in the disk that is causing your symptoms. Material from inside the disk is removed. Other fragments of the disk may also be removed.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
When one of your disks moves out of place (herniates), the soft gel inside pushes through the wall of the disk. The disk may then place pressure on the spinal cord and nerves that are coming out of your spinal column.
Many of the symptoms caused by a herniated disk get better or go away over time without surgery. Most people with low back or neck pain, numbness, or even mild weakness are often first treated with anti-inflammatory medicines, physical therapy, and exercise.
Only a few people with a herniated disk need surgery.
Your health care provider may recommend a diskectomy if you have a herniated disk and:
- Leg or arm pain or numbness that is very bad or is not going away, making it hard to do daily tasks
- Severe weakness in muscles of your arm, lower leg or buttocks
- Pain that spreads into your buttocks or legs
If you are having problems with your bowels or bladder, or the pain is so bad that strong pain medicines do not help, you will need to have surgery right away.
Risks
Risks of anesthesia and surgery in general are:
- Reactions to medicines
- Breathing problems
- Bleeding, blood clots, infection
Risks of this surgery are:
- Damage to the nerves that come out of the spine, causing weakness or pain that does not go away.
- Your back pain does not get better, or pain comes back later.
- Pain after surgery, if all the disk fragments are not removed.
- Spinal fluid may leak and cause headaches.
- The disk may bulge out again.
- Your spine may become more unstable and require more surgery.
- Infection that may require antibiotics, a longer hospital stay, or more surgery.
Before the Procedure
Tell your surgeon or nurse if:
- You are or could be pregnant.
- You are taking any medicines, including medicines, drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription.
- You have been drinking a lot of alcohol, more than 1 or 2 drinks a day.
Planning for your surgery:
- If you have diabetes, heart disease, or other medical conditions, your surgeon may ask you to see the provider who treats you for these conditions.
- If you smoke, it’s important to cut back or quit. Smoking can slow healing and increase the risk for blood clots. Ask your provider for help quitting smoking.
- If needed, prepare your home to make it easier to recover after surgery.
- Ask your surgeon if you need to arrange to have someone drive you home after your surgery.
During the week before your surgery:
- You may be asked to temporarily stop taking medicines that keep your blood from clotting. These medicines are called blood thinners. This includes over-the-counter medicines and supplements such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and vitamin E. Many prescription medicines are also blood thinners.
- Ask your surgeon which medicines you should still take on the day of surgery.
- Let your surgeon know about any illness you may have before your surgery. This includes COVID-19, a cold, flu, fever, herpes breakout, or other illness. If you do get sick, your surgery may need to be postponed.
On the day of the surgery:
- Follow instructions about when to stop eating and drinking.
- Take the medicines your surgeon told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Bring your cane, walker, or wheelchair if you have one already. Also bring shoes with flat, nonskid soles.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
After the Procedure
Your surgeon will ask you to get up and walk around as soon as your anesthesia wears off. Most people go home the day of surgery. Do not drive yourself home.
Follow instructions about how to care for yourself at home.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people have pain relief and can move better after surgery. Numbness and tingling should get better or disappear. Your pain, numbness, or weakness may not get better or go away if you had nerve damage before surgery, or if you have symptoms caused by other spinal conditions.
Further changes may occur in your spine over time and new symptoms may occur.
Talk with your provider about how to prevent future back problems.
References
Dixit R. Low back pain. In: Firestein GS, McInnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 47.
Gardocki RJ. Anatomic approaches to the spine. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 37.
Gardocki RJ, Park AL. Degenerative disorders of the thoracic and lumbar spine. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 39.
Ryu WHA, O’Toole JE. Cervical spine and cervicothoracic junction - anterior approach. In: Steinmetz MP, Berven SH, Benzel EC, eds. Benzel's Spine Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 109.
Version Info
Version: 2.0
Last reviewed on: 6/4/2025
Reviewed by: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
