Birth control and family planning
Contraception; Family planning and contraception; Coitus interruptus
Your choice of a birth control method depends on a number of factors, including your health, how often you have sex, and whether or not you want children.
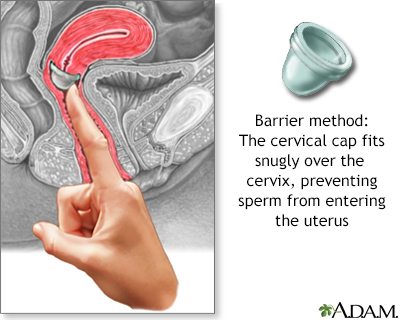
The cervical cap is a flexible rubber cup-like device that is filled with spermicide and self-inserted over the cervix prior to intercourse. The device is left in place several hours after intercourse. The cap is a prescribed device fitted by a health care professional and is more expensive than other barrier methods such as condoms.
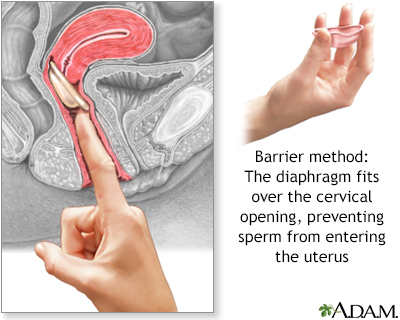
The diaphragm is a flexible rubber cup that is filled with spermicide and self-inserted over the cervix prior to intercourse. The device is left in place several hours after intercourse. The diaphragm is a prescribed device fitted by a health care professonal and is more expensive than other barrier methods such as condoms.
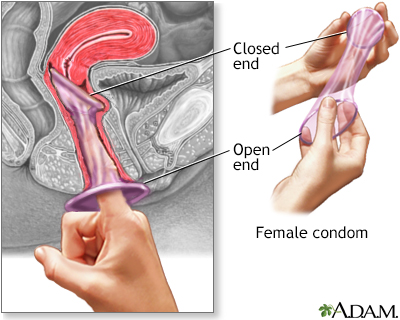
The female condom, like the male condom, is a barrier contraceptive made of latex or polyurethane. The condom has a ring on each end. The ring that is placed inside the vagina fits over the cervix, while the other ring, which is open, rests outside of the vagina and covers the vulva. The female condom is sold over-the-counter.
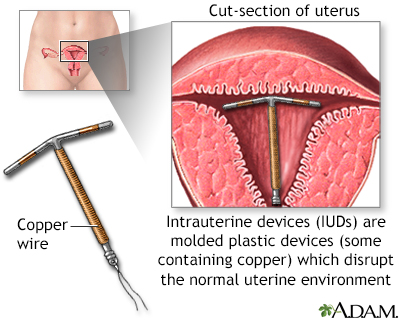
The intrauterine device shown uses copper as the active contraceptive, others use progesterone in a plastic device. IUDs are very effective at preventing pregnancy (less than 2% chance per year for the progesterone IUD, less than 1% chance per year for the copper IUD). IUDs come with increased risk of ectopic pregnancy and perforation of the uterus and do not protect against sexually transmitted disease. IUDs are prescribed and placed by health care providers.
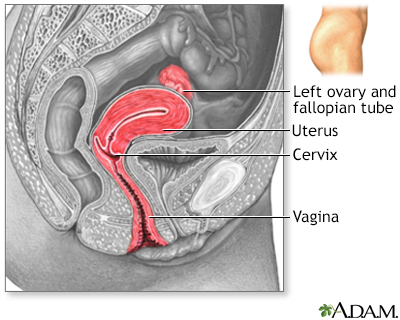
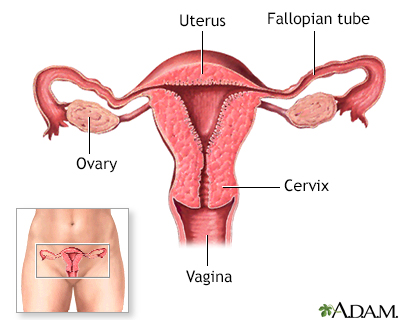
The female reproductive system includes the vagina, cervix, and uterus shown here in cut section.
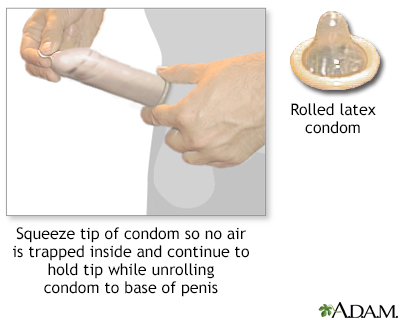
The male condom is a barrier contraceptive made of latex or polyurethane. The condom must be fitted over the erect penis. The condom is sold over-the-counter and when used properly is an inexpensive, effective barrier to pregnancy and sexually-transmitted disease.
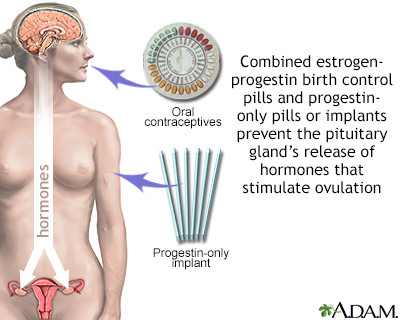
The pill works in several ways to prevent pregnancy. The pill suppresses ovulation so that an egg is not released from the ovaries, and changes the cervical mucus, causing it to become thicker and making it more difficult for sperm to swim into the womb. The pill also does not allow the lining of the womb to develop enough to receive and nurture a fertilized egg. This method of birth control offers no protection against sexually-transmitted diseases.
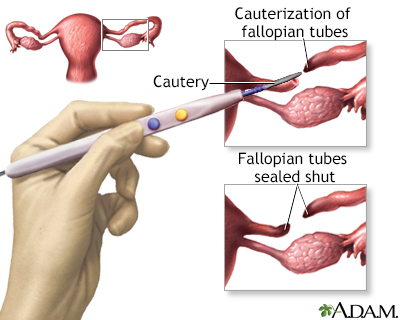
Surgical sterilization which permanently prevents the transport of the egg to the uterus by means of sealing the fallopian tubes is called tubal ligation, commonly called having one's tubes tied. This operation can be performed laparoscopically or in conjunction with a Cesarean section, after the baby is delivered. Tubal ligation is considered permanent but reversals can be done in many cases.
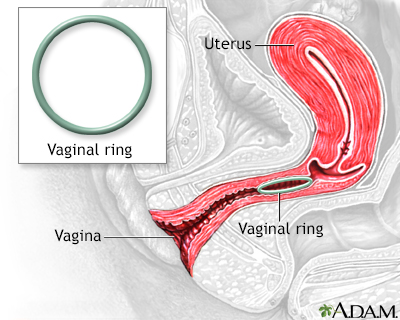
The vaginal ring is a flexible ring about 2 inches in diameter that is inserted into the vagina. It releases progestin and estrogen into the body to avoid pregnancy. The woman inserts it herself and it stays in the vagina for 3 weeks. Then, she takes it out for one week to have her period. Like other hormone methods, a prescription from a doctor is required.
During a normal monthly cycle, one of a woman's ovaries will produce a mature egg that will travel through the fallopian tube into the uterus. If sperm fertilizes this egg, the egg will attach itself to the uterine wall and begin developing into a fetus.
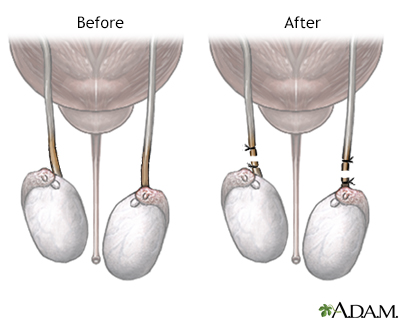
Vasectomy is a simple procedure that is very effective in preventing pregnancy. Men usually have no side effects from vasectomy, and no change in sexual performance or function. Some men will feel sore for a few days, but pain can be relieved by analgesics and an ice pack.
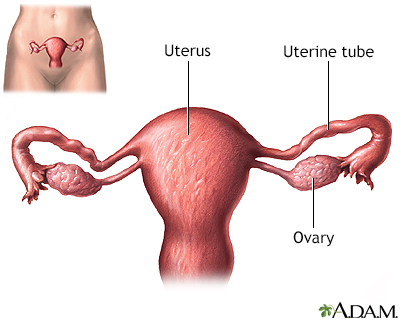
The ovaries are connected to the uterus by the uterine tubes (fallopian tubes). The egg travels through the tube to the uterus.
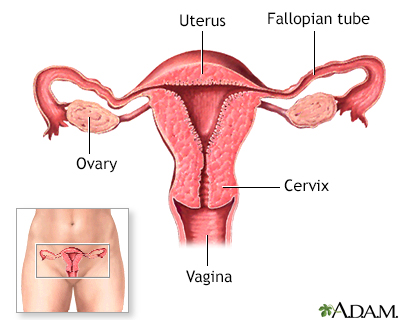
The internal female reproductive organs include the uterus, ovaries, cervix and vagina. These organs are necessary to produce a successful pregnancy. To prevent pregnancy, birth control pills affect how these organs normally function.
Information
Here are some questions to consider when selecting a birth control method:
- How well does the method prevent pregnancy? To tell how well a method works, look at the number of pregnancies in 100 women using that method over a period of 1 year.
- What are your feelings about getting pregnant? Would an unplanned pregnancy create hardship or distress to a woman or her partner? Or would a pregnancy be welcomed if it occurred earlier than planned?
- How much does a method of birth control cost? Does your insurance plan pay for it?
- What are the health risks? Talk about these risks with your health care provider before believing what you hear from others.
- Is your partner willing to accept and use a given method of birth control?
- Do you want a method that you only need to use when you have sex? Or do you want something that is in place and always working?
- Is preventing infections spread by sexual contact important? Many methods do not protect you from sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Condoms are the best choice for preventing STIs. They work best when combined with spermicides.
- Availability: Can the method be used without a prescription, a provider visit, or, in the case of minors, parental consent?
BARRIER METHODS OF BIRTH CONTROL
CONDOMS:
- A condom is a thin latex or polyurethane sheath. The male condom is placed around the erect penis. The female condom is placed inside the vagina before intercourse.
- A condom must be worn at all times during intercourse to prevent pregnancy.
- Condoms can be bought in most drug and grocery stores. Some family planning clinics offer free condoms. You do not need a prescription to get condoms.
DIAPHRAGM AND CERVICAL CAP:
- A diaphragm is a flexible rubber cup that is filled with spermicidal cream or jelly.
- It is placed into the vagina over the cervix before intercourse, to prevent sperm from reaching the uterus.
- It should be left in place for 6 to 8 hours after intercourse.
- Diaphragms must be prescribed by a woman's provider. The provider will determine the correct type and size of diaphragm for the woman.
- About 5 to 20 pregnancies occur over 1 year in 100 women using this method, depending on proper use.
- A similar, smaller device is called a cervical cap.
- Risks include irritation and allergic reactions to the diaphragm or spermicide, and increased frequency of urinary tract infection and vaginal yeast infection. In rare cases, toxic shock syndrome may develop in women who leave the diaphragm in too long. A cervical cap may cause an abnormal Pap test.
VAGINAL SPONGE:
- Vaginal contraceptive sponges are soft, and contain a chemical that kills or "disables" sperm.
- The sponge is moistened and inserted into the vagina, to cover over the cervix before intercourse.
- The vaginal sponge can be bought at your pharmacy without a prescription.
HORMONAL METHODS OF BIRTH CONTROL
Some birth control methods use hormones. They will have either both an estrogen and a progestin, or a progestin alone. You need a prescription for most hormonal birth control methods.
- Both hormones prevent a woman's ovary from releasing an egg during her cycle. They do this by affecting the levels of other hormones the body makes.
- Progestins help prevent sperm from making their way to the egg by making mucus around a woman's cervix thick and sticky.
Types of hormonal birth control methods include:
- Birth control pills: These may contain both estrogen and progestin, or only progestin.
- Implants: These are small rods implanted beneath the skin. They release a continuous dose of hormone to prevent ovulation.
- Progestin injections, such as Depo-Provera, that are given into the muscles of the upper arm or buttocks once every 3 months.
- The skin patch, such as Ortho Evra, is placed on your shoulder, buttocks, or other place on the body. It releases a continuous dose of hormones.
- The vaginal ring, such as NuvaRing, is a flexible ring about 2 inches (5 centimeters) wide. It is placed into the vagina. It releases the hormones progestin and estrogen.
- Emergency (or "morning after") contraception: This medicine can be bought without a prescription at your drugstore.
IUD (INTRAUTERINE DEVICE):
- The IUD is a small plastic or copper device placed inside the woman's uterus by her provider. Some IUDs release small amounts of progestin. IUDs may be left in place for 3 to 10 years, depending on the device used.
- IUDs can be placed at almost any time.
- IUDs are safe and work well. Fewer than 1 out of 100 women per year will get pregnant using an IUD.
- IUDs that release progestin may be for treating heavy menstrual bleeding and reducing cramps. They may also cause periods to stop completely.
PERMANENT METHODS OF BIRTH CONTROL
These methods are best for men, women, and couples who feel certain they do not want to have children in the future. They include vasectomy and tubal ligation. These procedures can sometimes be reversed if a pregnancy is desired at a later time. However, the success rate for reversal is not high.
BIRTH CONTROL METHODS THAT DO NOT WORK VERY WELL
- Withdrawal of the penis from the vagina before ejaculation can still result in pregnancy. Some semen often escapes before full withdrawal. It can be enough to cause a pregnancy.
- Douching shortly after sex is not likely to work. The sperm can make their way past the cervix within 90 seconds. Douching is never recommended because it can cause infections in the uterus and tubes.
- Breastfeeding: Despite the myths, women who are breastfeeding can become pregnant.
References
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists website. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 206: Use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133(6):1288. Erratum for: Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133(2):e128-e150. PMID: 31135757
Committee on Adolescent Health Care. Committee Opinion No 699: Adolescent pregnancy, contraception, and sexual activity. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129(5):e142-e149. PMID: 28426620
Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. US selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(4):1-66. PMID: 27467319
Harper DM, Wilfling LE, Blanner CF. Contraception. In: Rakel RE, Rakel DP, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 26.
Jatlaoui TC, Ermias Y, Zapata LB. Contraception. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 143.
Rivlin K, Davis AR. Contraception and abortion. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 13.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 1/10/2022
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
