Blood clots
Clot; Emboli; Thrombi; Thromboembolus; Hypercoagulable state
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid.
- A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is called a thrombus. A thrombus may also form in your heart.
- A thrombus that breaks loose and travels from one location in the body to another is called an embolus.
A thrombus or embolus can partly or completely block the flow of blood in a blood vessel.
- A blockage in an artery may prevent oxygen from reaching the tissues in that area. This is called ischemia. If ischemia is not treated promptly, it can lead to tissue damage or death.
- A blockage in the vein will often cause fluid buildup and swelling in the area where blood is drained by that vein.
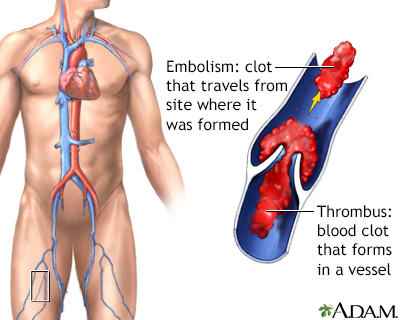
A thrombus is a blood clot that forms in a vessel and remains there. An embolism is a clot that travels from the site where it formed to another location in the body. Thrombi or emboli can lodge in a blood vessel and block the flow of blood in that location depriving tissues of normal blood flow and oxygen. This can result in damage, destruction (infarction), or even death of the tissues (necrosis) in that area.
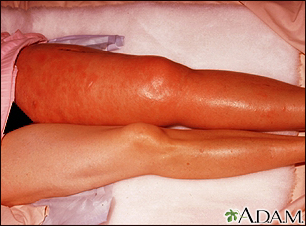
This picture shows a red and swollen thigh and leg caused by a blood clot (thrombus) in the deep veins in the groin (iliofemoral veins) which prevents normal return of blood from the leg to the heart.
Causes
Situations in which a blood clot is more likely to form in veins include:
- Being on long-term bed rest
- Sitting for long periods, such as in a plane or car
- During and after pregnancy
- Taking birth control pills or estrogen hormones (especially in women who smoke)
- Long-term use of an intravenous catheter
- After surgery
Blood clots are also more likely to form after an injury. People with cancer, obesity, and liver or kidney disease are also prone to blood clots.
Smoking also increases the risk of forming blood clots.
Conditions that are passed down through families (inherited) may make you more likely to form abnormal blood clots. Inherited conditions that affect clotting are:
- Factor V Leiden mutation
- Prothrombin G20210A mutation
Other rare conditions, such as protein C, protein S, and antithrombin III deficiencies.
A blood clot may block an artery or vein in an organ, affecting the:
- Heart (angina or a heart attack)
- Intestines (mesenteric ischemia or mesenteric venous thrombosis)
- Kidneys (renal vein thrombosis)
- Leg or arm arteries
- Legs (deep vein thrombosis)
- Lungs (pulmonary embolism)
- Neck or brain (stroke)
References
Anderson JA, Weitz JI. Hypercoagulable states. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 138.
Cross SS. Ischaemia, infarction and shock . In: Cross SS, ed. Underwood's Pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 7.
Schafer AI. Approach to the patient with bleeding or thrombosis: hypercoagulable states. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 157.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 6/17/2024
Reviewed by: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
