Intestinal obstruction
Paralytic ileus; Intestinal volvulus; Bowel obstruction; Ileus; Pseudo-obstruction - intestinal; Colonic ileus; Small bowel obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the bowel. The contents of the intestine cannot pass through it.
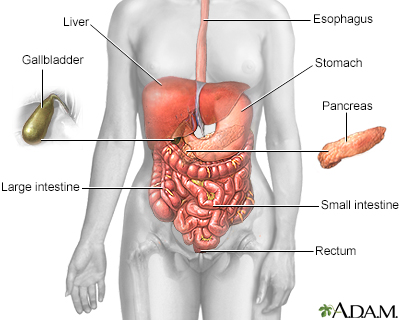
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
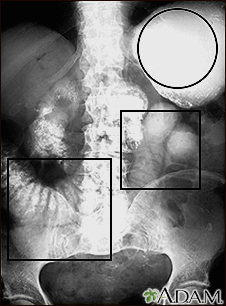
This abdominal X-ray shows a stomach filled with fluid and a swollen (distended) small bowel, caused by a blockage (pseudo-obstruction) in the intestines. A solution containing a dye (barium) that is visible on X-rays was swallowed by the patient (upper GI series).
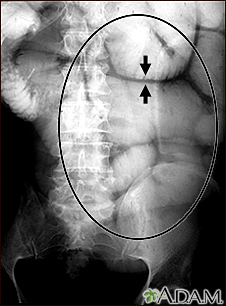
This abdominal X-ray shows thickening of the bowel wall and swelling (distention) caused by a blockage (pseudo-obstruction) in the intestines. A solution containing a dye (barium), which is visible on X-ray, was swallowed by the patient (the procedure is known as an upper GI series).
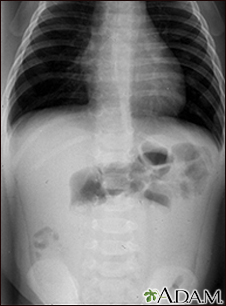
This abdominal X-ray shows an intestinal condition in which a loop of bowel has slipped into another section of bowel (intussusception), causing swelling, reduced blood flow, obstruction, and tissue damage. Intussusception requires emergency treatment (barium enema or surgery) to prevent intestinal tissue death (necrosis), intestinal perforation, peritonitis, and death.
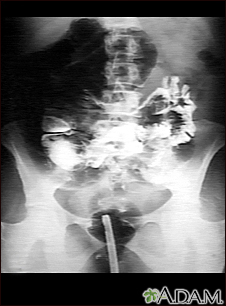
A GI series in a patient with a twisted bowel (volvulus).
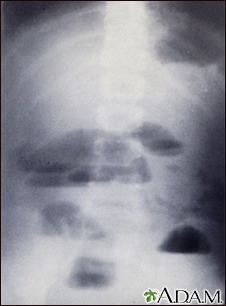
X-rays of the abdomen are important in diagnosing the presence of small bowel obstruction. When obstruction occurs, both fluid and gas collect in the intestine. They produce a characteristic pattern called air-fluid levels. The air rises above the fluid and there is a flat surface at the air-fluid interface.
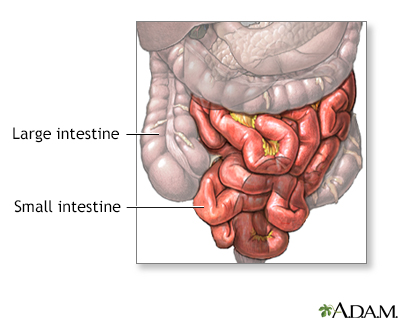
The small intestine absorbs much of the liquid from foods. There are three parts of the small intestine, the duodenum, the ileum and the jejunum.
Causes
Obstruction of the bowel may be due to:
- A mechanical cause, which means something is partially of fully blocking the bowel
- Ileus, a condition in which the bowel does not work correctly, but there is no structural problem causing the obstruction
Paralytic ileus, also called pseudo-obstruction, is one of the major causes of intestinal obstruction in infants and children. Causes of paralytic ileus may include:
- Bacteria or viruses that cause intestinal infections (gastroenteritis)
- Chemical, electrolyte, or mineral imbalances (such as decreased blood potassium level)
- Abdominal surgery
- Decreased blood supply to the intestines
- Infections inside the abdomen, such as appendicitis
- Kidney or lung disease
- Use of certain medicines, especially narcotics
Mechanical causes of intestinal obstruction may include:
- Adhesions or scar tissue that form after surgery
- Foreign bodies (objects that are swallowed and block the intestines)
- Gallstones (rare)
- Hernias
- Impacted stool
- Intussusception (telescoping of one segment of bowel into another)
- Tumors blocking the intestines
- Volvulus (twisted intestine)
- Inflammatory diseases such as Crohn disease
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Abdominal swelling (distention)
- Abdominal fullness, gas
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Breath odor
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Inability to pass gas
- Nausea and vomiting
Exams and Tests
During a physical exam, the health care provider may find bloating, tenderness, or hernias in the abdomen.
Tests that show obstruction include:
- Abdominal CT scan
- Abdominal x-ray
- Barium enema
- Upper GI and small bowel series
Treatment
Treatment involves placing a tube through the nose into the stomach or intestine. This is to help relieve abdominal swelling (distention) and vomiting. Volvulus of the large bowel may be treated by passing a tube into the rectum.
Surgery may be needed to relieve the obstruction if the tube does not relieve the symptoms. It may also be needed if there are signs of tissue death. If a tumor is causing a mechanical obstruction, surgery may be needed. Obstruction from inflammation such as Crohn disease may be treated with surgery, a procedure to dilate the narrow area, or medicine if inflammation is causing a blockage.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome depends on the cause of the blockage. Most of the time, the cause is successfully treated.
Possible Complications
Complications may include or may lead to:
- Electrolyte (blood chemical and mineral) imbalances
- Dehydration
- Hole (perforation) in the intestine
- Infection
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
If the obstruction blocks the blood supply to the intestine, it may cause infection and tissue death (gangrene). Risks for tissue death are related to the cause of the blockage and how long it has been present. Hernias, volvulus, and intussusception carry a higher gangrene risk.
In a newborn, paralytic ileus that destroys the bowel wall (necrotizing enterocolitis) is a life-threatening condition. It may lead to blood and lung infections.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you:
- Cannot pass stool or gas
- Have a swollen abdomen (distention) that does not go away
- Keep vomiting
- Have unexplained abdominal pain that does not go away
Prevention
Prevention depends on the cause. Treating conditions, such as tumors and hernias that can lead to a blockage, may reduce your risk.
Some causes of obstruction cannot be prevented.
References
Galandiuk S, Netz U, Morpurgo S, et al. Colon and rectum. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 52.
Gan T, Evers BM. Small intestine. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 50.
Mustain WC, Turnage RH. Intestinal obstruction. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 123.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 5/14/2024
Reviewed by: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
