Rheumatoid lung disease
Lung disease - rheumatoid arthritis; Rheumatoid nodules; Rheumatoid lung
Rheumatoid lung disease is a group of lung problems related to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The condition can include:
- Blockage of the small airways (bronchiolitis obliterans)
- Fluid in the chest (pleural effusions)
- High blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension)
- Lumps in the lungs (nodules)
- Scarring (pulmonary fibrosis)
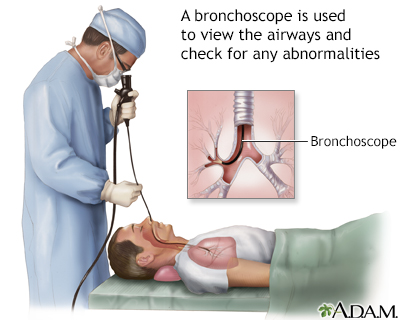
Bronchoscopy is a surgical technique for viewing the interior of the airways. Using sophisticated flexible fiber optic instruments, surgeons are able to explore the trachea, main stem bronchi, and some of the small bronchi. In children, this procedure may be used to remove foreign objects that have been inhaled. In adults, the procedure is most often used to take samples of (biopsy) suspicious lesions and for culturing specific areas in the lung.
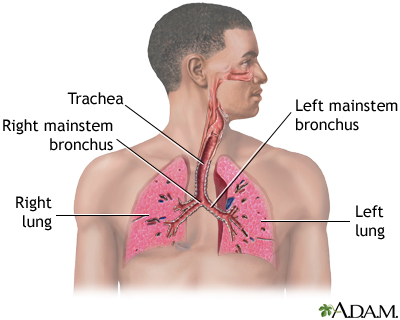
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Causes
Lung problems are common in RA. They often cause no symptoms, but for some people they are the main symptom of their RA.
The cause of lung disease associated with RA is unknown. Sometimes, the medicines used to treat RA, especially methotrexate, may result in lung disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling
- Skin nodules
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical examination and ask about your symptoms.
Symptoms depend on the type of lung disease RA is causing in the lungs.
When listening to the lungs with a stethoscope, your provider may hear normal breath sounds or:
- Crackles (rales)
- Decreased breath sounds
- Wheezing
- A rubbing sound
When listening to the heart, there may be abnormal heart sounds.
The following tests may show signs of rheumatoid lung disease:
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the chest
- Echocardiogram (may show pulmonary hypertension)
- Lung biopsy (bronchoscopic, video-assisted, or open)
- Lung function tests
- Needle inserted into the fluid around the lung (thoracentesis)
- Blood tests for rheumatoid arthritis
Treatment
Many people with this condition have no symptoms. Treatment is aimed at the health problems causing the lung problem and the complications caused by the disorder. Corticosteroids or other medicines that suppress the immune system are sometimes useful.
There is emerging evidence that pirfenidone and nintedanib may work for people with fibrosis due to rheumatoid lung disease.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Outcome is related to the underlying disorder and the type and severity of lung disease. In severe cases, lung transplantation can be considered. This is more common in cases of bronchiolitis obliterans, pulmonary fibrosis, or pulmonary hypertension.
Possible Complications
Rheumatoid lung disease may lead to:
- Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
- Pulmonary hypertension
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if you have rheumatoid arthritis and you develop unexplained breathing difficulties or worsening of baseline breathing difficulties.
References
Corte TJ, Wells AU. Connective tissue diseases. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 92.
Ozasa M, Fuluka J, Smith ML. Chronic diffuse lung diseases. In: Smith ML, Leslie KO, Wick MR, eds. Practical Pulmonary Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 8.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 5/3/2023
Reviewed by: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
