Transposition of the great vessels
d-TGA; Congenital heart defect - transposition; Cyanotic heart disease - transposition; Birth defect - transposition; Transposition of the great vessels; TGV
Transposition of the great arteries (TGA) is a heart defect that occurs from birth (congenital). The two major arteries that carry blood away from the heart -- the aorta and the pulmonary artery -- are switched (transposed).
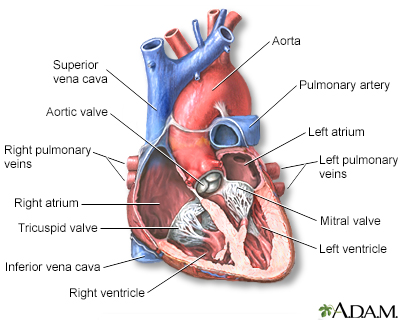
The interior of the heart is composed of valves, chambers, and associated vessels.
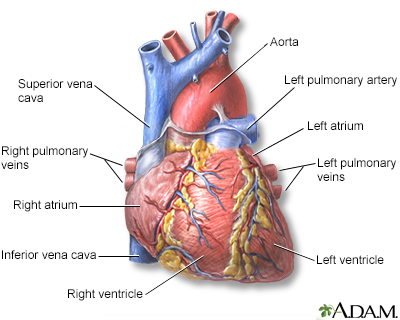
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
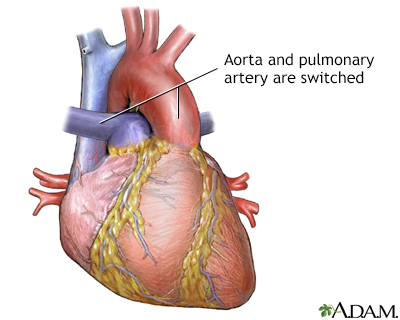
Transposition of the great vessels is a congenital heart defect in which the position of the two major vessels that carry blood away from the heart, the aorta and the pulmonary artery, is switched (transposed). This defect is classified as a cyanotic heart defect because the condition results in insufficiently oxygenated blood pumped to the body which leads to cyanosis (a bluish-purple coloration to the skin) and shortness of breath.
Causes
The cause of TGA is unknown. It is not associated with any one common genetic abnormality. It rarely occurs in other family members.
TGA is a cyanotic heart defect. This means there is decreased oxygen in the blood that is pumped from the heart to the rest of the body.
In normal hearts, blood that returns from the body goes through the right side of the heart and pulmonary artery to the lungs to get oxygen. The blood then comes back to the left side of the heart and travels out the aorta to the body.
In TGA, venous blood returns normally to the heart through the right atrium. But, instead of going to the lungs to absorb oxygen, this blood is pumped out through the aorta and back to the body. This blood has not been recharged with oxygen and leads to cyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms appear at birth or very soon afterward. How bad the symptoms are depends on the type and size of additional heart defects (such as atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, or patent ductus arteriosus) and how much the blood can mix between the two abnormal circulations.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Bluish color to the skin (cyanosis) due to low oxygen level in the blood
- Clubbing of the fingers or toes
- Poor feeding
- Shortness of breath
Exams and Tests
The health care provider may detect a heart murmur while listening to the chest with a stethoscope. The baby's mouth and skin will be a blue color.
Tests often include the following:
- Cardiac catheterization
- Chest x-ray
- ECG
- Echocardiogram (if done before birth, it is called a fetal echocardiogram)
- Pulse oximetry (to check blood oxygen level)
Treatment
The initial step in treatment is to allow oxygen-rich blood to mix with poorly oxygenated blood. The baby will immediately receive a medicine called prostaglandin through an IV (intravenous line). This medicine helps keep a blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus open, allowing some mixing of the two blood circulations. In some cases, an opening between the right and left atrium can be created with procedure using a balloon catheter. This allows blood to mix. This procedure is known as balloon atrial septostomy.
Permanent treatment involves heart surgery during which the great arteries are cut and stitched back to their correct position. This is called an arterial switch operation (ASO). Prior to the development of this surgery, a surgery called an atrial switch (or Mustard procedure or Senning procedure) was used.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The child's symptoms will improve after surgery to correct the defect. Most infants who undergo arterial switch do not have symptoms after surgery and live normal lives. If corrective surgery is not performed, the life expectancy is only months.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Coronary artery problems
- Heart valve problems
- Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
This condition can be diagnosed before birth using a fetal echocardiogram. If not, it is most often diagnosed soon after a baby is born.
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if your baby's skin develops a bluish color, especially in the face or trunk.
Contact your provider if your baby has this condition and new symptoms develop, get worse, or continue after treatment.
Prevention
Women who plan to become pregnant should be immunized against rubella if they are not already immune. Rubella infection in a pregnant woman can cause CHD.
Women who are pregnant should get good prenatal care:
- Avoid alcohol and illegal drugs during pregnancy.
- Tell your provider that you are pregnant before taking any new medicines.
- Have a blood test early in your pregnancy to see if you are immune to rubella. If you are not immune, avoid any possible exposure to rubella and get vaccinated right after delivery.
- Pregnant women who have diabetes should try to get good control over their blood sugar level.
References
Bernstein D. Cyanotic congenital heart disease: evaluation of the critically ill neonate with cyanosis and respiratory distress. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 456.
Valente AM, Dorfman AL, Babu-Narayan SV, Kreiger EV. Congenital heart disease in the adolescent and adult. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 82.
Well A, Fraser CD. Congenital heart disease. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 59.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 10/23/2023
Reviewed by: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
