Global Analysis Shows Cardiac Stents Beneficial in Women
World-Wide Study of More Than 11,000 Female Patients Provides Evidence that Stents Can Be Safe and Efficient in Women Who Are Traditionally Underrepresented in Clinical Trials
Cardiac stents to open blocked heart arteries and reduce chest pain have been used for decades. However, cardiologists have never been certain that women benefitted from their use because clinical trials testing stents only included, at most, 25 percent women, making the overall findings mostly relevant to just men.
But now a new world-wide pooled analysis, presented by researchers from The Mount Sinai Medical Center at the ESC Congress 2013 in Amsterdam, organized by the European Society of Cardiology, provides strong evidence that stents work well in women. Their examination of 26 randomized stent studies that enrolled 11,557 women concluded that women benefit just as much from stents as men do.
All of the different generations of stents were also deemed to be effective. However, researchers also found that the use of the newest drug-eluting stents (DES) in women were safer in comparison to earlier era DES and bare-metal stents.
"We are happy that our analysis showed promising results for women and found stents are beneficial in females. The magnitude of benefit seems to be in line with what the clinical trials show in the general population they studied, which was mostly men," reports the study's lead investigator, Roxana Mehran, MD, Director of Interventional Cardiovascular Research and Clinical Trials and Professor of Medicine in Cardiology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
"Whenever you have only 25 percent of a population, such as women, represented in clinical trials, you are really never sure of the safety and efficacy of a medical device in that population," says Dr. Mehran. "Clinically, women are not always the same as men."
It is not clear why more women were not enrolled in the clinical trials testing different generations of stents. "It may be that many women did not meet the clinical trial inclusion criteria because they are generally older when a stent is needed and because of age, they may have additional health issues that made them ineligible. Also, they may just have chosen not to participate," according to Dr. Mehran.
While the reason for the lack of female participation in stent clinical trials was not the focus of this new study, the critical issue could make a difference in how women have been ultimately treated for their heart disease over the years, according to study co-author Usman Baber, MD, Director of Clinical Biometrics and Assistant Professor of Medicine in Cardiology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
"There could very well be some reluctance by cardiologists in giving certain devices to women because of the lack of available safety and effectiveness data in the female population," Dr. Baber says.
"The results of our new analysis should provide reassurance to both physicians and female patients that the stent devices we are using have a similar efficacy and safety profile to what we have observed in men," says Dr. Baber.
In the ten year analysis of stent use, 10 percent of women received a bare-metal stent, 36 percent were given an earlier generation DES, and 54 percent received more advanced DES stents.
The investigators found that the three-year rates of death or heart attack among women treated with bare-metal stents, early generation DES, and newer generation DES, was 13 percent, 11 percent, and 9 percent, respectively. Rates of stent thrombosis — the development of a new clot — were 1 percent, 2 percent, and 1 percent, respectively. And the use of DES was also associated with a significant reduction in the need to reopen the artery — the range was 19 percent, 8 percent, and 6 percent, respectively.
Interestingly, this new gender analysis on stent use was generated by an extraordinary global collaboration. The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) launched and sponsored the Women in Innovation (WIN) Initiative, a world-wide effort devoted to improving treatment of women with cardiovascular disease.
Researchers from many countries came together at a one-day Gender Data Forum, sponsored by SCAI, WIN, and the American College of Cardiology (ACC), where Dr. Mehran and her research team discussed the lack of outcomes evidence regarding the use of stents in women.
"At the end of the day, researchers and industry sponsors agreed to share data on their clinical trials to pool together and examine the available scientific evidence about stent use in women," Dr. Mehran says. "This kind of global collaboration is unprecedented, and could serve as a future model to look at disease treatments for other populations who are underrepresented in clinical trials."
The study was generously funded by the Women in Innovation (WIN) Initiative.
Other study co-authors include: Samantha Sartori, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; Giulio G. Stefanini, MD, and Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern University Hospital; Marie-Claude Morice, MD, Institut Cardiovasculaire; Martin B. Leon, MD, Gregg W. Stone, MD, and Giora Weisz, MD, of NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center; Patrick W. Serruys, MD, PhD, Erasmus MC; William Wijns, MD, PhD, Cardiovascular Center Aalst; Edoardo Camenzind, MD, University of Geneva; Philippe G. Steg, MD, Département Hospitalo-Universitaire FIRE; Peter C. Smits, MD, Maasstad Hospital; David Kandzari, MD, Piedmont Heart Institute; Clemens Von Birgelen, MD, PhD, Thoraxcentrum Twente; Soren Galatius, MD, Gentofte University Hospital; Raban Jeger, MD, University Hospital Basel; Takeshi Kimura, MD, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine; Ghada Mikhail, MD, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust; Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, Hoag Memorial Hospital; Laxmi Mehta, MD, Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus; Rebecca Ortega, Society of Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions; Hyo-Soo Kim, MD, PhD, Seoul National University Main Hospital; Marco Valgimigli, MD, PhD, University of Ferrara; Adnan Kastrati, MD, Deutsches Herzzentrum, Munich; and Alaide Chieffo, MD, San Raffaele Hospital.
About The Mount Sinai Medical Center
The Mount Sinai Medical Center encompasses both The Mount Sinai Hospital and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Established in 1968, the Icahn School of Medicine is one of the leading medical schools in the United States, with more than 3,400 faculty in 32 departments and 14 research institutes. It ranks among the top 20 medical schools both in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and by U.S. News & World Report. The Mount Sinai Hospital, founded in 1852, is a 1,171-bed tertiary- and quaternary-care teaching facility and one of the nation's oldest, largest and most-respected voluntary hospitals. The Mount Sinai Hospital is nationally ranked by U.S. News & World Report as one of the top 25 hospitals in 7 specialties based on reputation, safety, and other patient-care factors.
For more information, visit http://www.mountsinai.org/.
Find Mount Sinai on:
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/mountsinainyc
Twitter @mountsinainyc
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with 48,000 employees working across eight hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2024-2025.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
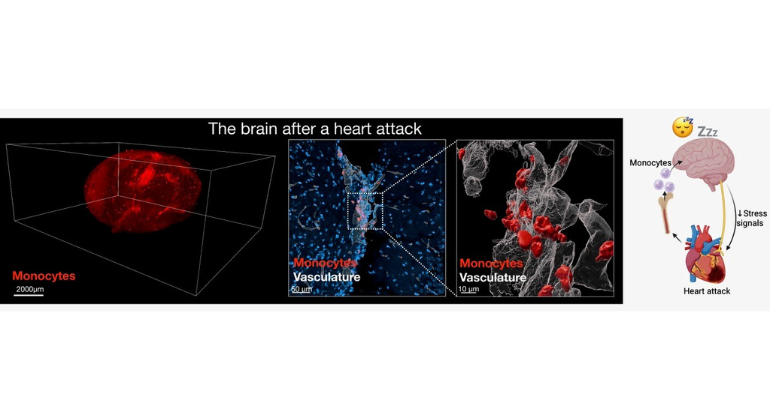
After a Heart Attack, the Heart Signals to the Brain to Increase Sleep to Promote Healing
Oct 30, 2024 View All Press Releases