Novel Nanotherapy Breakthrough May Help Reduce Recurrent Heart Attacks and Stroke
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai designs HDL nanoparticle to deliver statin medication inside inflamed blood vessels to prevent repeat heart attacks and stroke.
Up to 30 percent of heart attack patients suffer a new heart attack because cardiologists are unable to control inflammation inside heart arteries — the process that leads to clots rupturing and causing myocardial infarction or stroke.
But a report in Nature Communications by Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai scientists showcases the development of a new technology that may provide a solution to this high risk of repeat heart attacks — and potentially help save more lives.
An international research team, led by Mount Sinai investigators, designed and tested a high-density lipoprotein (HDL) nanoparticle loaded with a statin drug. In mouse studies, they show this HDL nanotherapy is capable of directly targeting and lowering dangerous inflammation in blood vessels.
Not only could the HDL nanotherapy potentially avert repeat heart attacks, it may also have the power to reduce recurrent strokes caused by clots in brain arteries, says the study's senior investigator, Willem Mulder, PhD, Associate Professor of Radiology in the Translational and Molecular Imaging Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
"We envision that a safe and effective HDL nanotherapy could substantially lower cardiovascular events during the critical period of vulnerability after a heart attack or stroke," says Dr. Mulder.
"While we have much more to do to confirm clinical benefit in patients, our study shows how this nanotherapy functions biologically, and how this novel concept could potentially also work in the clinical setting to solve a critical problem," says Dr. Mulder. "This nanotherapy would be the first of its kind."
Inject HDL Statin Nanotherapy Right After Heart Attack and Stroke Treatment
The research team, led by two PhD graduate students as first authors — Raphael Duivenvoorden, MD, and Jun Tang, MS— fashioned the nanoparticle to resemble an HDL cholesterol particle. In fact, the nanoparticle binds on to the same receptors as natural HDL in order to deliver the statin drug.
Oral statin medications used by millions of people today work primarily in the liver to reduce levels of unhealthy lipids, such as low density lipoproteins (LDL), that circulate in the blood. Statins also exert a very weak dampening effect on some inflammatory cells, foremost those called macrophages that hide within plaque in the arterial walls.
It is this anti-inflammatory function that the researchers sought to bolster by designing their HDL nanotherapy.
Inflammation is the main driver of plaque buildup in arteries. Without inflammation, as well as lipid deposition in blood vessels, clots would not form. As inflammation progresses, macrophages secrete enzymes that degrade the walls of blood vessels, leading to a break in the vessel and the formation of clots. These clots can then clog arteries, leading to a heart attack or stroke.
"Levels of inflammation spike after a heart attack, which is why up to 30 percent of heart attack patients may suffer another heart attack, some while in hospital or just after discharge," says co-author Zahi Fayad, PhD, Professor of Radiology and Director of the Translational and Molecular Imaging Institute at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. "This is the vital time to attack this inflammation culprit, which we currently are unable to do clinically right now," says Dr. Fayad. "Even with the most aggressive treatment available, repeat heart attacks do occur."
According to Mount Sinai researchers, the best way to use their HDL nanotherapy is by injection after the clot that produces a heart attack or stroke has been treated. The HDL nanoparticle would deliver the statin directly to macrophages that are driving the inflammatory response. "This could potentially and very rapidly stabilize a dangerous situation," Dr. Mulder says. "In addition, after discharge, patients would continue to use their oral statins to control LDL in their blood."
"Our study also confirms that the HDL nanoparticle is not seen as a foreign invader by the body's immune system and that it has an inherent and natural affinity to target plaque macrophages," says Jun Tang. "Our experiments demonstrated a very rapid reduction in inflammation in mice with advanced plaque buildup."
If the HDL nanotherapy works well in clinical studies, it may be possible to use it in the future as a heart attack prevention tool, according to Dr. Fayad. "If proven to be safe and effective in humans, this would be a critical advance for cardiovascular medicine. We look forward to further testing of our team's novel nanotherapy breakthrough."
The study was primarily supported by the NHLBI, NIH, as a Program of Excellence in Nanotechnology (PEN) Award (HHSN268201000045C) as well as the NIH grants (R01 EB009638, K99 EB012165, R01 CA155432, P01HL098055, R01HL084312), an American Heart Association grant (13PRE14350020-Founders), and a NWO grant (ZonMW Vidi 91713324).
The international research team includes co-authors from Mount Sinai: Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD (also, of Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares in Madrid, Spain), David P. Cormode, Aneta J. Mieszawska, David Izquierdo-Garcia, Canturk Ozcan, Maarten J. Otten, Neeha Zaidi, Mark E. Lobatto, Sarian M. van Rijs, Bram Priem, and Emma L. Kuan. Other co-authors include: Catherine Martel and Gwendalyn J. Randolph of the Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri; Edward A. Fisher and Bernd Hewing (Medizinische Klinik fu¨r Kardiologie und Angiologie, Campus Mitte, Charite´–Universitaetsmedizin Berlin, Germany) of the Department of Medicine (Cardiology) and Cell Biology, Marc and Ruti Bell Program in Vascular Biology at NYU School of Medicine; Hendrik Sager and Matthias Nahrendorf of Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Center for Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts; and Erik S.G. Stroes of Department of Vascular Medicine, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, employing 48,000 people across its hospitals and more than 400 outpatient practices, as well as more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2024-2025.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
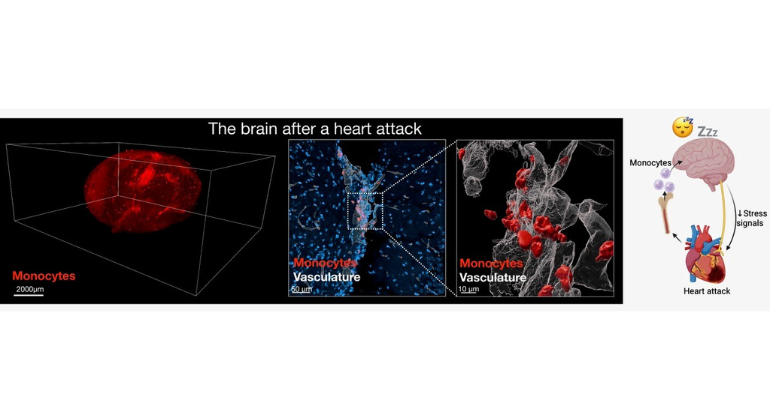
After a Heart Attack, the Heart Signals to the Brain to Increase Sleep to Promote Healing
Oct 30, 2024 View All Press Releases