Stopping Aspirin One Month After Coronary Stenting Procedures Significantly Reduces Bleeding Complications in Heart Attack Patients
Breakthrough study led by Mount Sinai researcher could change standard-of-care guidelines to improve outcomes

Withdrawing aspirin one month after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in high-risk heart patients and keeping them on ticagrelor alone safely improves outcomes and reduces major bleeding by more than half when compared to patients taking aspirin and ticagrelor combined (also known as dual antiplatelet therapy or DAPT), which is the current standard of care.
These are the results from the ULTIMATE-DAPT study announced during a late-breaking trial presentation at the American College of Cardiology Scientific Sessions on Sunday, April 7, and published in The Lancet.
This is the first and only trial to test high-risk patients with recent or threatened heart attack (acute coronary artery syndromes, or ACS) taking ticagrelor with a placebo starting one month after PCI, and compare them with ACS patients taking ticagrelor with aspirin over the same period. The significant findings could change the current guidelines for standard of care worldwide.
“Our study has demonstrated that withdrawing aspirin in patients with recent ACS one month after PCI is beneficial by reducing major and minor bleeding through one year by more than 50 percent. Moreover, there was no increase in adverse ischemic events, meaning continuing aspirin was causing harm without providing any benefit,” says Gregg W. Stone, MD, the study co-chair of ULTIMATE-DAPT, who presented the trial results.
“It is my belief that it’s time to change the guidelines and standard clinical practice such that we no longer treat most ACS patients with dual antiplatelet therapy beyond one month after a successful PCI procedure. Treating these high-risk patients with a single potent platelet inhibitor such as ticagrelor will improve prognosis,” adds Dr. Stone, who is Director of Academic Affairs for the Mount Sinai Health System and Professor of Medicine (Cardiology), and Population Health Science and Policy, at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The study analyzed 3,400 patients with ACS at 58 centers in four countries between August 2019 and October 2022. All of the patients had undergone PCI, a non-surgical procedure in which interventional cardiologists use a catheter to place stents in the blocked coronary arteries to restore blood flow. The patients were stable one month after PCI and were on ticagrelor and aspirin. Researchers randomized the patients after one month, withdrawing aspirin in 1,700 patients and putting them on ticagrelor and a placebo, while leaving the other 1,700 patients on ticagrelor and aspirin. All patients were evaluated between 1 and 12 months after the procedure.
During the study period, 35 patients in the ticagrelor-placebo group had a major or minor bleeding event, compared to 78 patients in the ticagrelor-aspirin group, meaning that the incidence of overall bleeding incidents was reduced by 55 percent by withdrawing aspirin. The study also analyzed major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events including death, heart attack, stroke, bypass graft surgery, or repeat PCI. These events occurred in 61 patients in the ticagrelor-placebo group compared to 63 patients in the ticagrelor-aspirin group, and were not statistically significant - further demonstrating that removing aspirin did no harm and improved outcomes.
“It was previously believed that discontinuing dual antiplatelet therapy within one year after PCI in patients with ACS would increase the risk of heart attack and other ischemic complications, but the present study shows that is not the case, with contemporary drug-eluting stents now used in all PCI procedures. Discontinuing aspirin in patients with a recent or threatened heart attack who are stable one month after PCI is safe and, by decreasing serious bleeding, improves outcomes,” Dr. Stone adds. “This study extends the results of prior work that showed similar results but without the quality of using a placebo, which eliminates bias from the study.”
This trial was funded by the Chinese Society of Cardiology, the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China, and Jiangsu Provincial & Nanjing Municipal Clinical Trial Project.
Figure: Primary efficacy and safety outcomes during follow-up between one-month and 12-months post-PCI
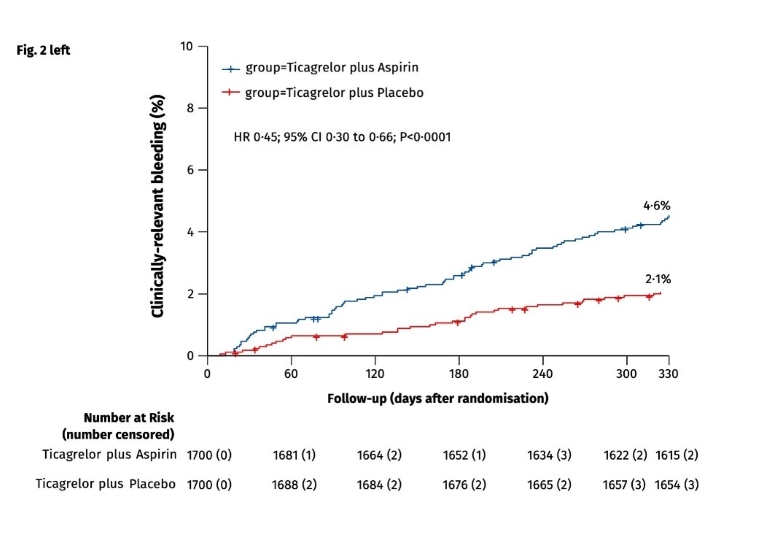
Left: The primary efficacy endpoint of clinically-relevant bleeding, defined as BARC types 2, 3 or 5 bleeding, was assessed in the intention-to-treat population between one-month and twelve-months post-PCI in patients who were event-free after one month of ticagrelor and aspirin. Switching to ticagrelor monotherapy at one month resulted in a 55-percent reduction in the hazard of clinically relevant bleeding compared with continuing ticagrelor plus aspirin over the ensuing 11 months.
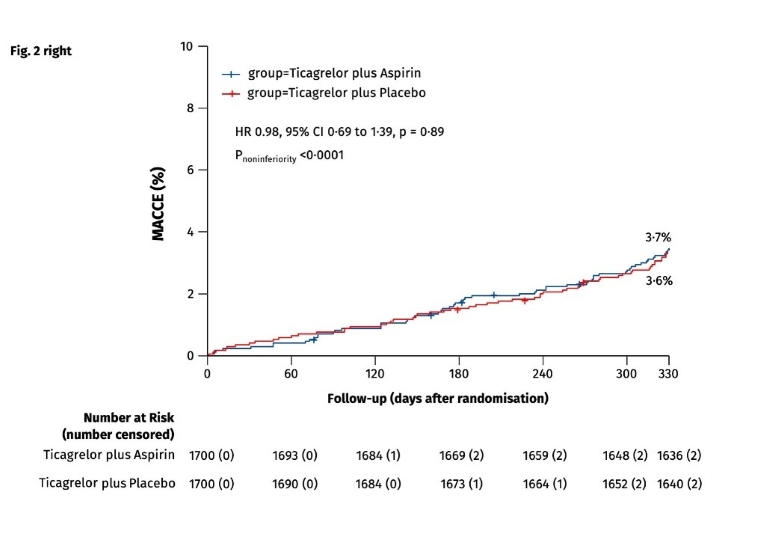
Right: The primary safety endpoint of MACCE, the composite cardiac death, myocardial infarction, ischaemic stroke, definite stent thrombosis, or clinically-driven target vessel revascularization, was assessed in the intention-to-treat population between one-month and 12-months post-PCI in patients who were event-free after one month of ticagrelor and aspirin. During the next eleven months patients treated with ticagrelor monotherapy had similar rates of adverse ischaemic events as patients who were maintained on ticagrelor plus aspirin.
PCI denotes percutaneous coronary intervention; BARC denotes Bleeding Academic Research Consortium; MACCE, major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Mount Sinai is a World Leader in Cardiology and Heart Surgery
Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital at The Mount Sinai Hospital ranks No. 1 in New York and No. 4 globally according to Newsweek’s “The World’s Best Specialized Hospitals.” It also ranks No. 1 in New York for cardiology, heart, and vascular surgery, according to U.S. News & World Report®.
It is part of Mount Sinai Health System, which is New York City's largest academic medical system, encompassing eight hospitals, a leading medical school, and a vast network of ambulatory practices throughout the greater New York region. We advance medicine and health through unrivaled education and translational research and discovery to deliver care that is the safest, highest-quality, most accessible and equitable, and the best value of any health system in the nation. The Health System includes approximately 7,400 primary and specialty care physicians; 13 joint-venture outpatient surgery centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida; and more than 30 affiliated community health centers. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2023-2024.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, employing 48,000 people across its hospitals and more than 400 outpatient practices, as well as more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2024-2025.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.

Inter-Atrial Shunts May Benefit Some Heart Failure Patients While Harming Others
Apr 06, 2024 View All Press Releases

.jpg)
