Acute pancreatitis
Gallstone pancreatitis; Pancreas - inflammation
Acute pancreatitis is sudden swelling and inflammation of the pancreas.
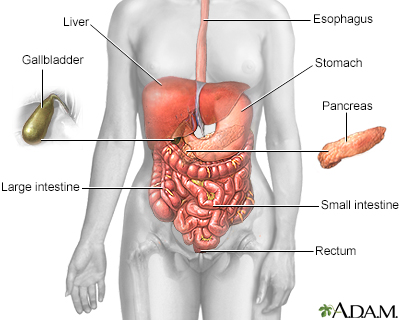
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
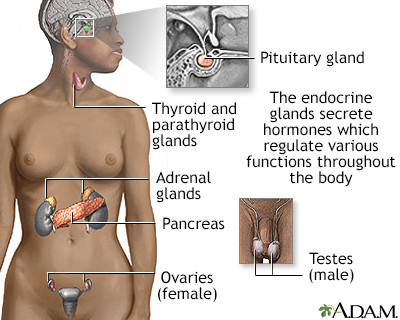
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
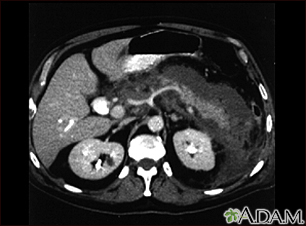
This upper abdominal CT scan shows inflammation and swelling of the pancreas caused by acute infection (pancreatitis).
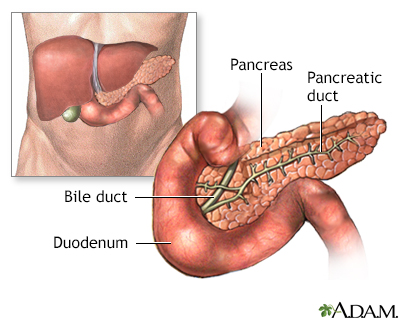
The pancreas is located in the upper part of the abdomen, behind the stomach. It contains cells that secrete the hormone insulin, and cells that secrete digestive enzymes that aid in the breakdown of food in the gastrointestinal tract. The pancreas secretes these enzymes into the pancreatic duct, which joins the common bile duct from the liver and drains into the small intestine.
Causes
The pancreas is an organ located behind the stomach. It produces the hormones insulin and glucagon. It also produces chemicals called enzymes needed to digest food.
Most of the time, the enzymes are active only after they reach the small intestine.
- If these enzymes become active inside the pancreas, they can digest the tissue of the pancreas. This causes swelling, bleeding, and damage to the organ and its blood vessels.
- This problem is called acute pancreatitis.
Acute pancreatitis affects men more often than women. Certain diseases, surgeries, and habits make you more likely to develop this condition.
- Alcohol use is responsible for up to 70% of cases in the United States. About 5 to 8 drinks per day for 5 or more years can damage the pancreas.
- Gallstones are the next most common cause. When the gallstones travel out of the gallbladder into the bile ducts, they may block the opening that drains bile and enzymes. The bile and enzymes "back up" into the pancreas and cause swelling.
- Genetics may be a factor in some cases. Sometimes, the cause is not known.
Other conditions that have been linked to pancreatitis are:
- Autoimmune problems (when the immune system attacks the body)
- Damage to the bile ducts or pancreas during surgery
- High blood levels of a fat called triglycerides -- most often above 1,000 mg/dL
- Injury to the pancreas from an accident
Other causes include:
- After certain procedures used to diagnose gallbladder and pancreas problems (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, ERCP) or ultrasound guided biopsy
- Cystic fibrosis
- Overactive parathyroid gland
- Reye syndrome
- Use of certain medicines (especially estrogens, corticosteroids, sulfonamides, thiazides, and azathioprine)
- Certain infections, such as mumps, that involve the pancreas
Symptoms
The main symptom of pancreatitis is pain felt in the upper left side or middle of the abdomen. The pain:
- May be worse within minutes after eating or drinking at first, more commonly if foods have a high fat content
- Becomes constant and more severe, lasting for several days
- May be worse when lying flat on the back
- May spread (radiate) to the back or below the left shoulder blade
People with acute pancreatitis often look ill and have a fever, nausea, vomiting, and sweating.
Other symptoms that may occur with this disease include:
- Clay-colored stools
- Bloating and fullness
- Hiccups
- Indigestion
- Mild yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Swollen abdomen
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a physical exam, which may show:
- Abdominal tenderness or lump (mass)
- Fever
- Low blood pressure
- Rapid heart rate
- Rapid breathing (respiratory) rate
Lab tests that show the release of pancreatic enzymes will be done. These include:
- Increased serum amylase level
- Increased serum lipase level (a more specific indicator of pancreatitis than amylase levels)
- Increased urine amylase level
Other blood tests that can help diagnose pancreatitis or its complications include:
The following imaging tests that can show swelling of the pancreas may be done, but are not always needed to make a diagnosis of acute pancreatitis:
Treatment
Treatment often requires a stay in the hospital. It may involve:
- Pain medicines
- Fluids given through a vein (IV)
- Stopping food or fluid by mouth to limit the activity of the pancreas. In the past, patients did not get food for many days. However, feeding the digestive tract is an important treatment for pancreatitis, therefore a feeding tube may be put into the stomach or intestine until you can eat by mouth again.
A tube may be inserted through the nose or mouth to remove the contents of the stomach. This may be done if vomiting and severe pain do not improve. The tube will stay in for 1 to 2 days to 1 to 2 weeks.
Treating the condition that caused the problem can prevent repeated attacks.
In some cases, therapy is needed to:
- Drain fluid that has collected in or around the pancreas
- Remove gallstones
- Relieve blockages of the pancreatic duct
In the most severe cases, surgery is needed to remove damaged, dead or infected pancreatic tissue.
Avoid smoking, alcoholic drinks, and fatty foods after the attack has improved.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most cases go away in a week or less. However, some cases develop into a life-threatening illness.
The death rate is high when:
- Bleeding in the pancreas has occurred.
- Liver, heart, or kidney problems are also present.
- An abscess forms the pancreas.
- There is death or necrosis of larger amounts of tissue in the pancreas.
Sometimes the swelling and infection do not fully heal. Repeat episodes of pancreatitis may also occur. Either of these can lead to long-term damage of the pancreas (called chronic pancreatitis).
Possible Complications
Pancreatitis can return. The chances of it returning depend on the cause, and how well it can be treated. Complications of acute pancreatitis may include:
- Acute kidney failure
- Long-term lung damage (due to adult respiratory distress syndrome or ARDS)
- Buildup of fluid in the abdomen (ascites)
- Fluid collections in the pancreas (pancreatic pseudocysts) that may become infected (pancreatic abscess)
- Heart failure
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have intense, constant abdominal pain.
- You develop other symptoms of acute pancreatitis.
Prevention
You may lower your risk of new or repeat episodes of pancreatitis by taking steps to prevent the medical conditions that can lead to the disease:
- DO NOT drink alcohol if it is the likely cause of the acute attack.
- DO NOT smoke. Tobacco smoking can worsen acute and chronic pancreatitis.
- Make sure children receive vaccines to protect them against mumps and other childhood illnesses.
- Treat medical problems that lead to high blood levels of triglycerides.
References
Crockett SD, Wani S, Gardner TB, Falck-Ytter Y, Barkun AN. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on initial management of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(4):1096-1101. PMID: 29409760
Forsmark CE. Pancreatitis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 130.
Tenner S, Vege SS, Sheth SG, et al. American College of Gastroenterology Guidelines: management of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2024 1;119(3):419-437. Epub 2023 Nov 7. PMID: 38857482.
Van Buren G, Fisher WE. Acute and chronic pancreatitis. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, Heidelbaugh JJ, Lee EM, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2024. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:175-182.
Vege SS. Acute pancreatitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 58.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 12/31/2023
Reviewed by: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
