Fecal fat
Quantitative stool fat determination; Fat absorption
The fecal fat test measures the amount of fat in the stool. This can help gauge the percentage of dietary fat that the body does not absorb.
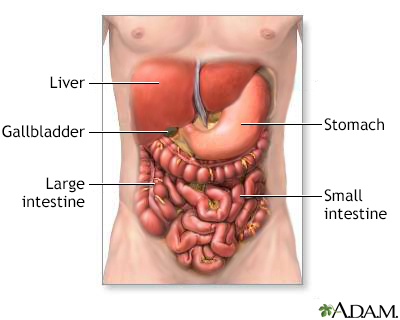
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
How the Test is Performed
There are many ways to collect the samples.
- For adults and children, you can catch the stool on plastic wrap loosely placed over the toilet bowl and held in place by the toilet seat. Then put the sample in a clean container. One test kit supplies a special toilet tissue that you use to collect the sample, then put the sample in a clean container.
- For infants and children wearing diapers, you can line the diaper with plastic wrap. If the plastic wrap is placed properly, you can prevent mixing of urine and stool. This will provide a better sample.
Collect all stool that is released over a 24-hour period (or sometimes 3 days) in the containers provided. Label the containers with name, time, and date, and send them to the lab.
Sometimes you will be asked to provide a single stool sample to be examined under a microscope for stool fat.
How to Prepare for the Test
Eat a normal diet containing about 100 grams (g) of fat per day for 3 days before starting the test. The health care provider may ask you to stop using medicines or food additives that could affect the test.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves only normal bowel movements. There is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
This test evaluates fat absorption to tell how well the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and intestines are working.
Fat malabsorption can cause a change in your stools called steatorrhea. To absorb fat normally, the body needs bile from the gallbladder (or the liver if the gallbladder has been removed), enzymes from the pancreas, and a normal small intestine.
Normal Results
Less than 7 g of fat per 24 hours.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Decreased fat absorption may be caused by:
- Biliary tumor
- Biliary stricture
- Celiac disease (non-tropical sprue)
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Crohn disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Gallstones (cholelithiasis)
- Pancreatic cancer
- Pancreatitis
- Radiation enteritis
- Short bowel syndrome (for example from surgery or an inherited problem)
- Small bowel bacterial overgrowth
- Whipple disease
Risks
There are no risks.
Considerations
Factors that interfere with the test are:
- Enemas
- Laxatives
- Mineral oil
- Inadequate fat in diet prior to and during the stool collection
References
Höegenauer C, Hammer HF. Maldigestion and malabsorption. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 104.
Semrad CE. Approach to the patient with diarrhea and malabsorption. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 126.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 8/12/2024
Reviewed by: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Gastroenterologist, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
