Bronchoscopy
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy; Lung cancer - bronchoscopy; Pneumonia - bronchoscopy; Chronic lung disease - bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
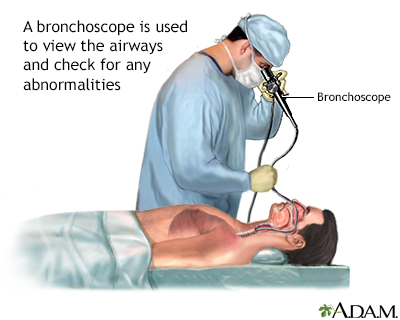
Bronchoscopy is a surgical technique for viewing the interior of the airways. Using sophisticated flexible fiber optic instruments, surgeons are able to explore the trachea, main stem bronchi, and some of the small bronchi. In children, this procedure may be used to remove foreign objects that have been inhaled. In adults, the procedure is most often used to take samples of (biopsy) suspicious lesions and for culturing specific areas in the lung.
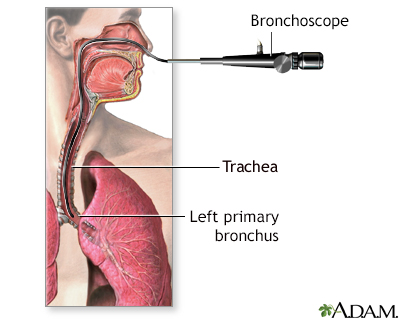
A bronchoscope is a tube with a tiny camera on the end which is inserted through the nose (or mouth) into the lungs. During a bronchoscopy procedure, a scope will be inserted through the nostril until it passes through the throat into the trachea and bronchi. A bronchoscope is used to provide a view of the airways of the lung (tracheobronchial tree). The scope also allows the doctor to collect lung secretions and lung tissue for biopsy for tissue specimens.
How the Test is Performed
A bronchoscope is a device used to see the inside of the airways and lungs. The scope can be flexible or rigid. A flexible scope is almost always used. It is a tube less than one half inch (1.27 centimeter) wide and about 2 feet (60 centimeters) long. In rare cases, a rigid bronchoscope is used.
- You will likely get medicines through a vein (IV, or intravenously) to help you relax. Or, you may be asleep under general anesthesia, especially if a rigid scope is used.
- A numbing medicine (anesthetic) will be sprayed in your mouth and throat. If bronchoscopy is done through your nose, numbing jelly will be placed in the nostril the tube goes through.
- The scope is gently inserted. It will likely make you cough at first. The coughing will stop as the numbing medicine begins to work.
- Your health care provider may send saline solution through the tube. This washes the lungs and allows your provider to collect samples of lung cells, fluids, microbes and other materials inside the air sacs. This part of the procedure is called a lavage.
- Sometimes, tiny brushes, needles, or forceps may be passed through the bronchoscope to take very small tissue samples (biopsies) from your lungs.
- Your provider can also place a stent in your airway or view your lungs with ultrasound during the procedure. A stent is a small tube-like medical device. Ultrasound is a painless imaging method that allows your provider to see inside your body.
- Sometimes ultrasound is used to see the lymph nodes and tissues around your airways, and small needles can be inserted there to obtain tissue and make certain diagnoses.
- At the end of the procedure, the scope is removed.
How to Prepare for the Test
Follow instructions on how to prepare for the test. You will likely be told:
- Not to eat or drink anything for 6 to 12 hours before your test.
- Not to take aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, or other blood-thinning medicines before your procedure. Ask the provider who will do your bronchoscopy if and when to stop taking these medicines.
- Arrange for a ride to and from the hospital.
- Arrange for help with work, child care, or other tasks, as you will likely need to rest the next day.
The test is most often done as an outpatient procedure, and you will go home the same day. Rarely, some people may need to stay overnight in the hospital.
How the Test will Feel
Local anesthetic is used to relax and numb your throat muscles. Until this medicine begins to work, you may feel fluid running down the back of your throat. This may cause you to cough or gag.
Once the medicine takes effect, you may feel pressure or mild tugging as the tube moves through your windpipe. Although you may feel like you are not able to breathe when the tube is in your throat, there is no risk of this happening. The medicines you receive to relax will help with these symptoms. You will likely forget most of the procedure.
When the anesthetic wears off, your throat may be scratchy for several days. After the test, your ability to cough (cough reflex) will return in 1 to 2 hours. You will not be allowed to eat or drink until your cough reflex returns.
Why the Test is Performed
You may have a bronchoscopy to help your provider diagnose lung problems. Your provider will be able to inspect your airways or take a biopsy sample.
Common reasons to do a bronchoscopy for diagnosis are:
- An imaging test showed abnormal changes of your lung, such as a growth or tumor, changes or scarring of lung tissue, or collapse of one area of your lung.
- To biopsy lymph nodes near your lungs.
- To see why you are coughing up blood.
- To explain shortness of breath or low oxygen levels.
- To see if there is a foreign object in your airway.
- You have a cough that has lasted more than 3 months without any clear cause.
- You have an infection in your lungs and major airways (bronchi) that cannot be diagnosed any other way or need a certain type of diagnosis.
- You inhaled a toxic gas or chemical.
- To see if lung rejection after a lung transplant is occurring.
You may also have a bronchoscopy to treat a lung or airway problem. For example, it may be done to:
- Remove fluid or mucus plugs from your airways
- Remove a foreign object from your airways
- Widen (dilate) an airway that is blocked or narrowed
- Drain an abscess
- Treat cancer using a number of different techniques
- Wash out an airway
Normal Results
Normal results mean normal cells and fluids are found. No foreign substances or blockages are seen.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Many disorders can be diagnosed with bronchoscopy, including:
- Infections from bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, or tuberculosis.
- Lung damage related to allergic-type reactions.
- Lung disorders in which the deep lung tissues become inflamed due to the immune system response, and then damaged. For example, changes from sarcoidosis or rheumatoid arthritis may be found.
- Lung cancer, or cancer in the area between the lungs.
- Narrowing (stenosis) of the trachea or bronchi.
- Acute rejection or infection after a lung transplant.
Risks
The main risks of bronchoscopy are:
- Bleeding from biopsy sites (most dangerous complication in very rare occasions)
- Infection
There is also a small risk for:
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Breathing difficulties
- Fever
- Heart attack, in people with existing heart disease
- Low blood oxygen
- Collapsed lung
- Sore throat
Risks when general anesthesia is used include:
- Muscle pain
- Change in blood pressure
- Slower heart rate
- Nausea and vomiting
References
Christie NA. Operative otolaryngology: bronchoscopy. In: Myers EN, Snyderman CH, eds. Operative Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 18.
Kupeli E, Mehta AC. Diagnostic bronchoscopy. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 26.
Weinberger SE, Cockrill BA, Mandel J. Evaluation of the patient with pulmonary disease. In: Weinberger SE, Cockrill BA, Mandel J, eds. Principles of Pulmonary Medicine. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 3.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 5/3/2024
Reviewed by: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
