Decaffeinated Coffee Improves Brain Energy Metabolism in an Animal Study
Mount Sinai researchers have found that decaffeinated coffee may reduce impaired brain energy metabolism associated with type 2 diabetes, a known risk factor for neurocognitive disorders.
Researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine have discovered that decaffeinated coffee may improve brain energy metabolism associated with type 2 diabetes. This brain dysfunction is a known risk factor for dementia and other neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease. The research is published online in Nutritional Neuroscience.
A research group led by Giulio Maria Pasinetti, MD, PhD, Professor of Neurology, and Psychiatry, at Mount Sinai School of Medicine, explored whether dietary supplementation with a standardized decaffeinated coffee preparation prior to diabetes onset might improve insulin resistance and glucose utilization in mice with diet-induced type 2 diabetes. The researchers administered the supplement for five months, and evaluated the brain's genetic response in the mice. They found that the brain was able to more effectively metabolize glucose and use it for cellular energy in the brain. Glucose utilization in the brain is reduced in people with type 2 diabetes, which can often result in neurocognitive problems.
"Impaired energy metabolism in the brain is known to be tightly correlated with cognitive decline during aging and in subjects at high risk for developing neurodegenerative disorders," said Dr. Pasinetti. "This is the first evidence showing the potential benefits of decaffeinated coffee preparations for both preventing and treating cognitive decline caused by type 2 diabetes, aging, and/or neurodegenerative disorders."
Coffee intake is not recommended for everybody due to the fact that it is associated with cardiovascular health risks such as elevated blood cholesterol and blood pressure, both of which lead to an increased risk for heart disease, stroke, and premature death. These negative effects have primarily been attributed to the high caffeine content of coffee. Nonetheless, these novel findings are evidence that some of the non-caffeine components in coffee provide health benefits in mice. Dr. Pasinetti hopes to explore the preventive role of decaffeinated coffee delivered as a dietary supplement in humans.
"In light of recent evidence suggesting that cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer's disease and other age-related neurodegenerative disorders may be traced back to neuropathological conditions initiated several decades before disease onset, developing preventive treatments for such disorders is critical," he said.
About The Mount Sinai Medical Center
The Mount Sinai Medical Center encompasses both The Mount Sinai Hospital and Mount Sinai School of Medicine. Established in 1968, Mount Sinai School of Medicine is one of the leading medical schools in the United States. The Medical School is noted for innovation in education, biomedical research, clinical care delivery, and local and global community service. It has more than 3,400 faculty in 32 departments and 14 research institutes, and ranks among the top 20 medical schools both in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and by US News and World Report.
The Mount Sinai Hospital, founded in 1852, is a 1,171-bed tertiary- and quaternary-care teaching facility and one of the nation's oldest, largest and most-respected voluntary hospitals. In 2011, US News and World Report ranked The Mount Sinai Hospital 16th on its elite Honor Roll of the nation's top hospitals based on reputation, safety, and other patient-care factors. Of the top 20 hospitals in the United States, Mount Sinai is one of 12 integrated academic medical centers whose medical school ranks among the top 20 in NIH funding and US News and World Report and whose hospital is on the US News and World Report Honor Roll. Nearly 60,000 people were treated at Mount Sinai as inpatients last year, and approximately 560,000 outpatient visits took place.
For more information, visit http://www.mountsinai.org/.
Find Mount Sinai on:
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/mountsinainyc
Twitter: @mountsinainyc
YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/mountsinainy
# # #
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with 48,000 employees working across seven hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2024-2025.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, X, and YouTube.
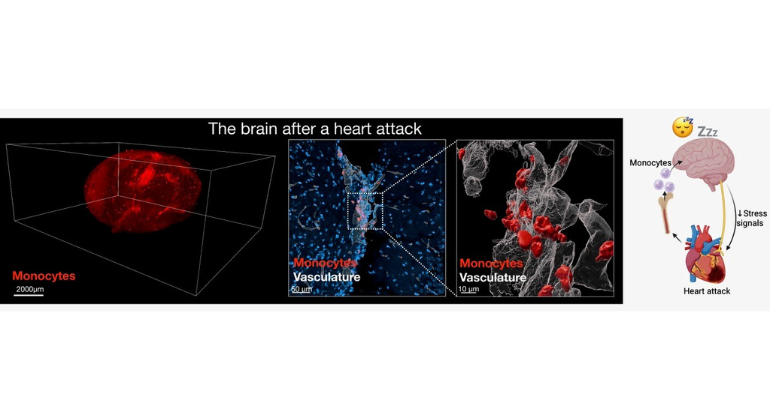
After a Heart Attack, the Heart Signals to the Brain to Increase Sleep to Promote Healing
Oct 30, 2024 View All Press Releases